FIG. 6.
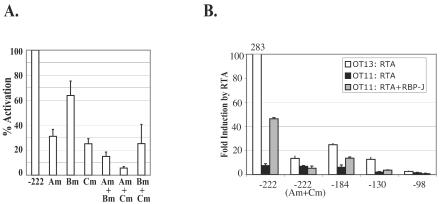
RBP-J plays a central role in RTA-mediated activation of the K14/vGPCR promoter. (A) Reporter construct pGL3-222 contains all three major RTA response elements, A, B, and C. Single mutation of site A, B, or C is indicated by Am, Bm, and Cm, respectively; corresponding double mutants are indicated by Am+Bm, Am+Cm, and Bm+Cm. The fold activation by RTA on each mutant was determined, normalized against that for the WT construct pGL3-222, and plotted as percent activation. The error bars represent standard deviations of the results from at least two independent experiments. (B) Comparison of RTA activation of the K14/vGPCR promoter constructs in OT13 (WT) and OT11 (RBP-J−/−) cells. OT13 or OT11 cells were transfected with 0.6 μg of individual K14/vGPCR reporter constructs [pGL3-222, pGL3-222(Am+Cm), pGL3-184, pGL3-130, or pGL3-98], 0 to 0.6 μg of RTA expression vector, and 0 to 0.6 μg of RBP-J expression vector (in OT11 cells only). pcDNA3.1-lacZ was included in each transfection as an internal control, and total DNA was normalized to 2 μg with vector pcDNA3.1. The fold induction by RTA was plotted, with the error bars representing standard deviations of the results from at least two independent experiments.
