Fig. 8.
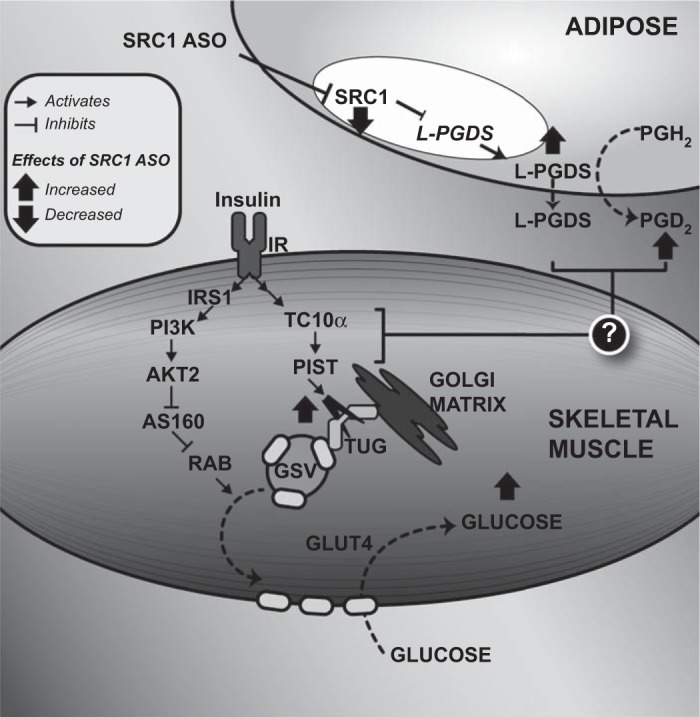
Schematic diagram showing the effect of SRC1 ASO on adipose tissue lipocalin type PGD2 synthase (L-PGDS) expression and muscle insulin-mediated glucose transport. SRC1 ASO decreases the expression of the transcription factor SRC1, leading to an increase in L-PGDS expression and secretion. L-PGDS then increases PGD2 synthesis, and L-PGDS, PGD2, or both lead to proteolysis of TUG proteins in insulin-stimulated gastrocnemius muscle. Since intact TUG prevents exocytic translocation of GLUT4 storage vesicles (GSV), the decrease in TUG abundance releases intracellular GLUT4 to fuse with the plasma membrane and to facilitate glucose transport in the presence of insulin (2). Therefore, SRC1 knockdown in the WAT enhances insulin-mediated glucose transport in the muscle. PGH2, prostaglandin H2; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate-1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AS160, Akt substrate of 160 kDa; RAB, Ras homologous from brain; PIST, PDZ domain-containing protein that interacts specifically with TC10α.
