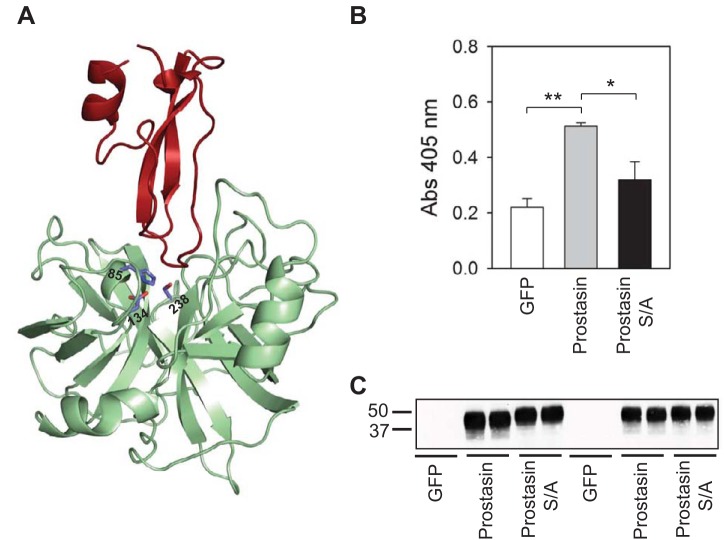
Fig. 2.
Mutant S/A prostasin is catalytically inactive. A: cartoon representation of a prostasin-aprotinin complex (Protein Database code 3GYM). His85, Asp134, and Ser238 in the catalytic triad of prostasin (green) are shown. Aprotinin is colored in red. B: amidolytic activity was assessed in culture media from human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293H cells transfected with green fluorescent protein (GFP), prostasin, or mutant S/A prostasin as described in experimental procedures. Amidolytic activity was significantly greater in media collected from HEK-293H cells transfected with prostasin than media collected from cells expressing GFP or mutant S/A prostasin. Statistically significant differences are indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (n = 4) by ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test. Amidolytic activity in media collected from HEK-293H cells transfected with GFP was not significantly different than in media collected from cells expressing mutant S/A prostasin. C: prostasin secretion in media collected from HEK-293H cells transfected with GFP, wild-type prostasin, or mutant S/A prostasin. The presence of secreted wild-type and mutant prostasin in the media was assessed by IB. Numbers on the left of the image represent the mobility of Bio-Rad Precision Plus protein standards (in kDa). Data are representative of four independent experiments.