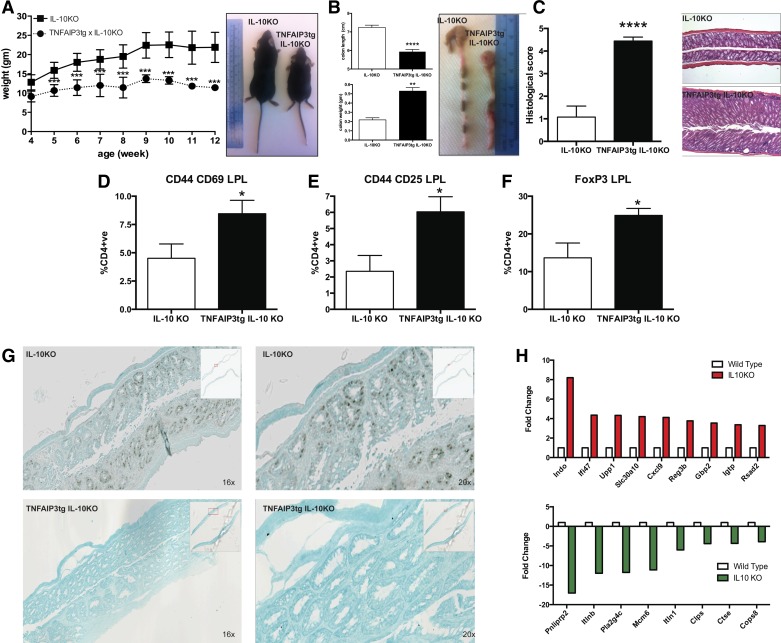
Fig. 1.
Epithelial expression of tumor necrosis factor-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) suppresses NF-κB activation and induces colitis in IL-10 knockout (KO) mice. Villin-TNFAIP3 transgenic mice (TNFAIP3tg) were interbred with IL-10−/− mice, and littermates were assessed for the activation of epithelial cell NF-κB and incidence and severity of colitis. TNFAIP3tg × IL-10KO, compared with IL-10KO mice, exhibited reduced body weight and failure to thrive apparent by 4 wk, significant by 5 wk of age (A); reduced length, increased weight, and visible turgidity of the colon (B); increased histological signs of inflammation (C); increased levels of activated CD4 T cells (D and E); and increased levels of FoxP3+ CD4 T cells in the colonic mucosa (F). G: reduced immunostaining for activated NF-κB (phospho-NF-κB) in the nuclei of epithelial cells. H: altered gene expression in the intestinal mucosa of noncolitic IL-10−/− mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.001.