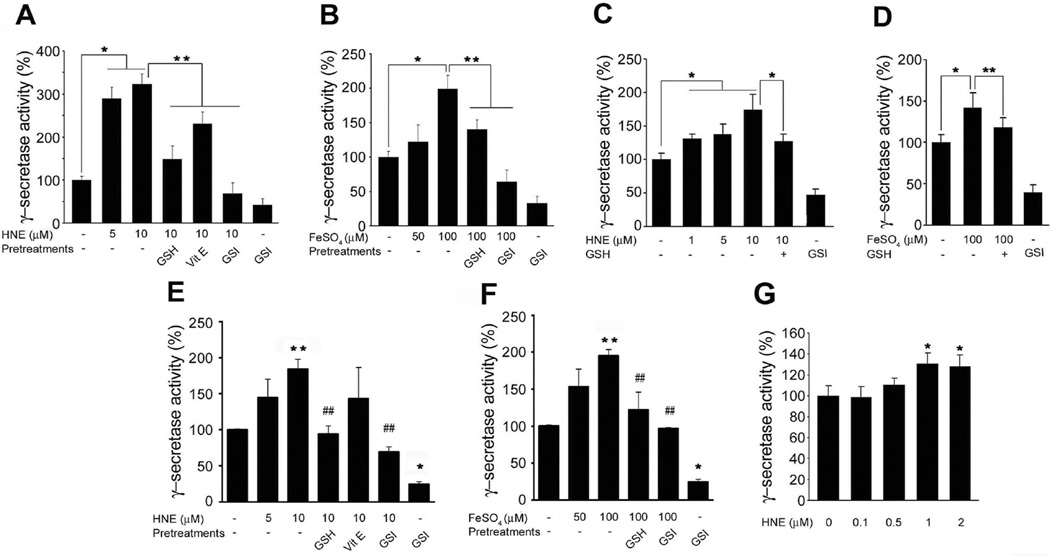
Figure 1.
The lipid peroxidation product HNE enhances γ-secretase activity. Cultured rat cortical neurons (A and B), hippocampal neurons (C and D), and SH-SY5Y cells (E and F) were pre-incubated with 500 µM glutathione-ethyl ester (GSH) or 2 µM γ-secretase inhibitor (GSI) for 1 h, or with vitamin E (50 ng/ml) for 24 h before being treated with HNE. Cells were collected after 3 h of incubation with HNE or FeSO4. Lysates of primary cultured cortical (A and B) and hippocampal (C and D) neurons were tested for γ-secretase activity. Values are the mean ± S.D. of at least 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.05. (E and F) SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with the constructs of C99-GVP with UAS-luciferase reporter gene. Cells were collected after 3h of incubation with HNE or FeSO4. Values are the mean ± S.D. of at least 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.05 vs. controls. ##p < 0.05 vs. HNE or FeSO4 treated samples. (G) Total extracts of 2×108 SH-SY5Y cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-PS1 antibody. Immunoprecipitants were incubated with HNE at 37 °C for 30 min and analyzed for γ-secretase activity in vitro. Values are the mean ± S.D. of at least 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.01 vs. non-treated control.