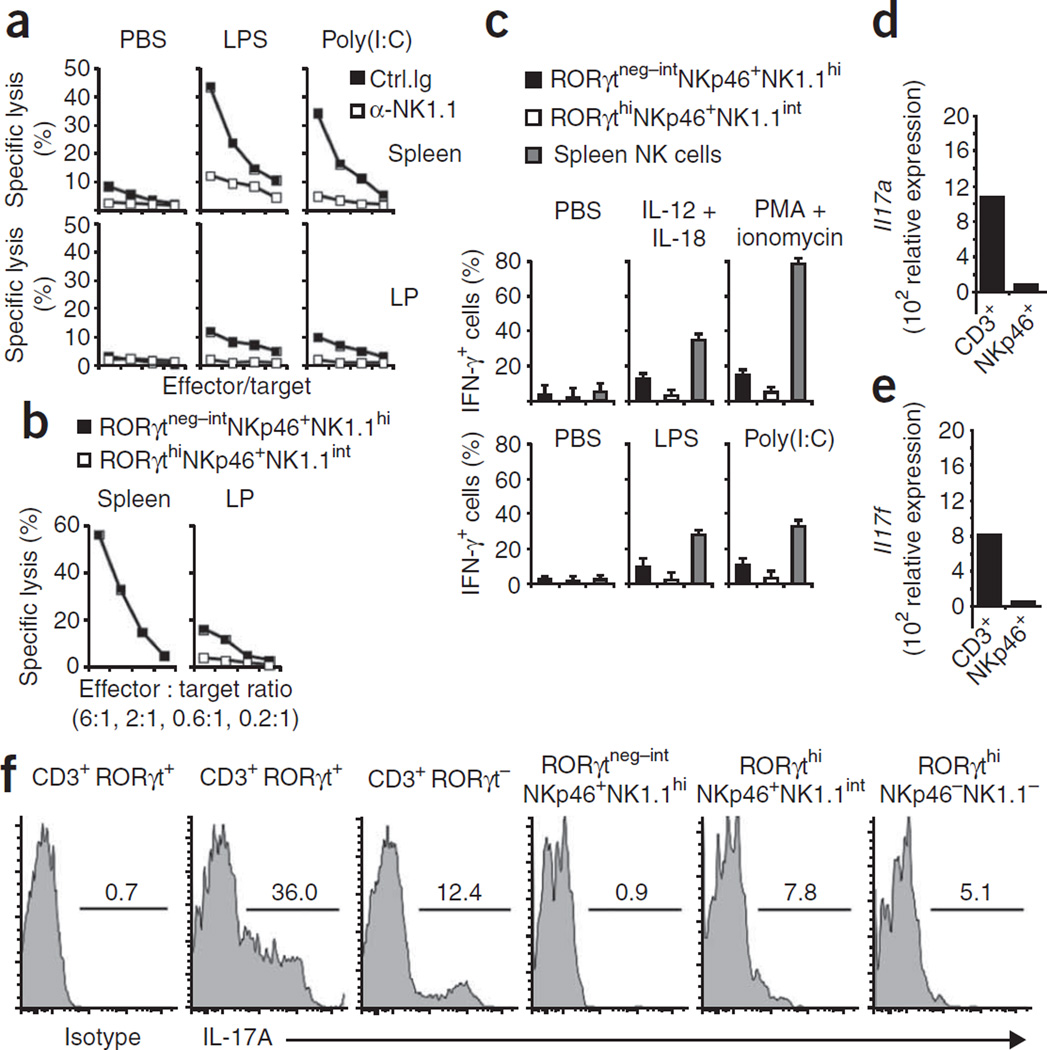
Figure 4.
Mucosal NKp46+ cells have only weak NK cell effector functions. (a) Cytotoxicity of lamina propria lymphocytes or splenocytes from B6 mice injected twice with anti-NK1.1 or isotype-matched control antibody and, 1 d later, with PBS, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (Poly(I:C)), assessed 24 h later as killing of YAC-1 mouse lymphoma target cells at effector/target ratios of 6:1, 2:1, 0.6:1 and 0.1:1. (b) Cytotoxicity of sorted lamina propria lymphocyte populations (RORγtneg–intNKp46+NK1.1hi and RORγthiNKp46+NK1.1int) or splenocyte cells (RORγt−NKp46+NK1.1+) from Rorc(γt)GFP/+ mice injected with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid, assessed 1 d later as killing of YAC-1 target cells. (c) IFN-γ-producing cells among Rorc(γt)GFP/+ lamina propria lymphocyte and splenocyte populations (key) incubated for 6 h in the presence of brefeldin A with various stimuli (above graphs) and then stained with anti-IFN-γ (top row), and IFN-γ-producing cells among lamina propria and spleen cells from Rorc(γt)GFP/+ mice injected with various Toll-like receptor ligands (above graphs) and, 1 d later, incubated for 6 h with YAC-1 cells in the presence of brefeldin A and then stained with anti-IFN-γ (bottom row). (d,e) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the expression of IL-17A mRNA (Il17a; d) and IL-17F mRNA (Il17f; e) in sorted lamina propria CD3+ and NKp46+CD3− (NKp46+) cells. (f) Flow cytometry of Rorc(γt)GFP/+ lamina propria cells stained with anti-CD3, anti-NK1.1 or anti-IL-17 or isotype-matched control antibody, gated on subsets above plots. Numbers above lines indicate percent IL-17+ cells. Data are representative of four (a), three (b–e) or five (f) independent experiments.