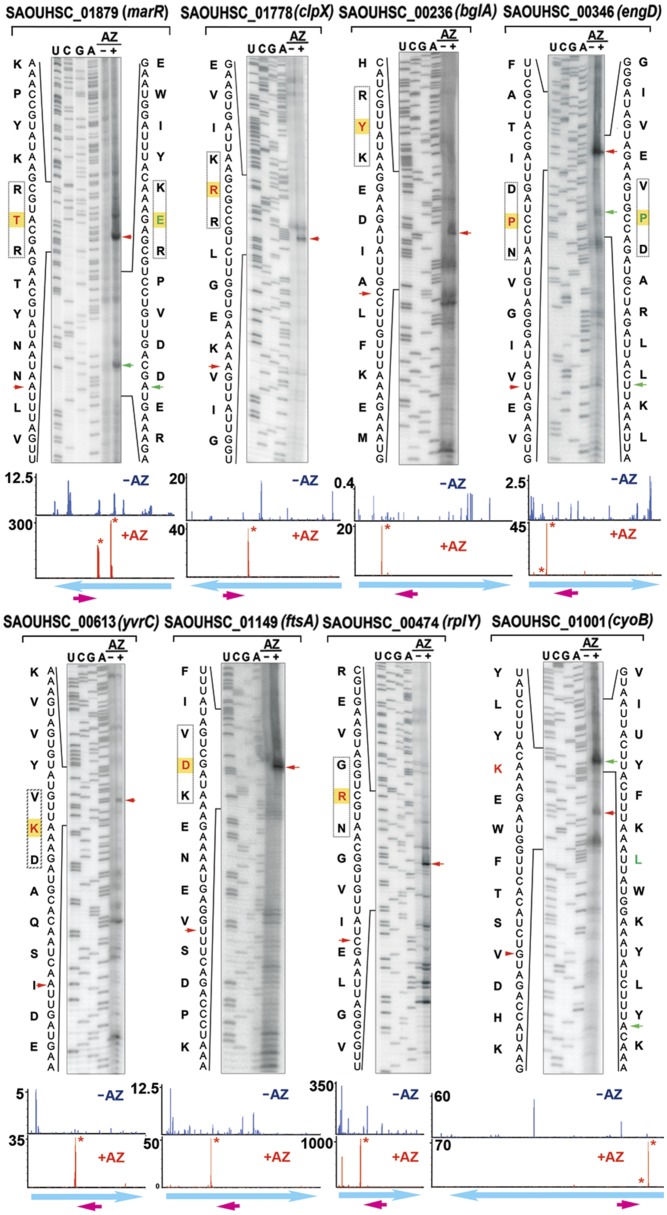
Fig. 3.
In vitro mapping of AZ-specific ribosome stalling sites by toe-printing analysis. Cell-free translation was programmed with the respective DNA templates in the presence and absence of AZ, followed by primer extension. Tripeptide stalling sequences are boxed. The residues labeled in red and green are positioned in the P site of the stalled ribosome, which are located 16–17 nt upstream of the blocked reverse transcriptase. Red and green arrowheads mark the primary and secondary toe-print signals. The ribosome density maps corresponding to the genes are shown on the bottom panels. The y axis indicates RPM-normalized ribosome density. The magenta arrows indicate the location of the reverse primer. The stalling sites are labeled with an asterisk. Weaker density peaks might not be visible owing to the scale difference.