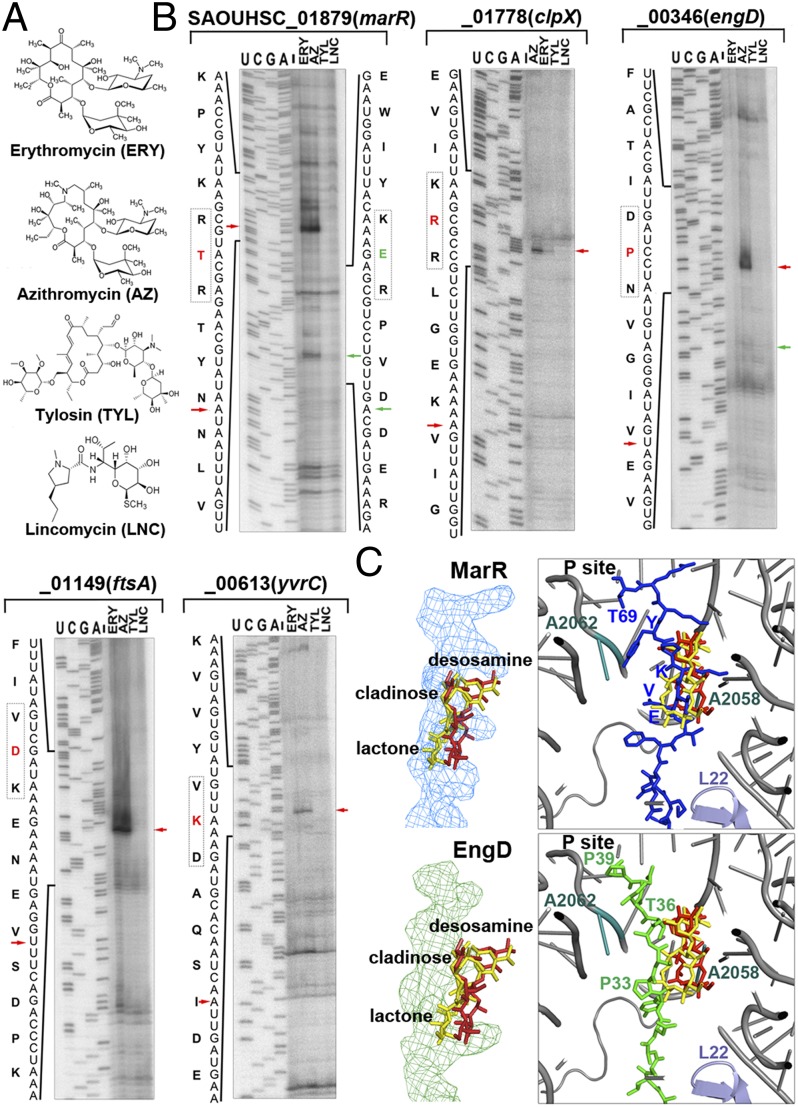
Fig. 4.
Distinct dispositions of MarR and EngD peptides inside the tunnel affect stalling efficiency. (A) Chemical structures of macrolides (ERY, AZ, and tylosin) and lincomycin. (B) Toe-printing analysis of representative stalling sequences in the presence of different antibiotics. Labeling schemes are identical to those of Fig. 3. (C) Structural modeling of the MarR and EngD stalling peptides inside the antibiotic-bound tunnel. The relative locations of previously reported ribosome stalling “sensors” (L22, A2062, and A2058) to the superimposed ERY (red) and AZ (yellow) molecules are indicated.