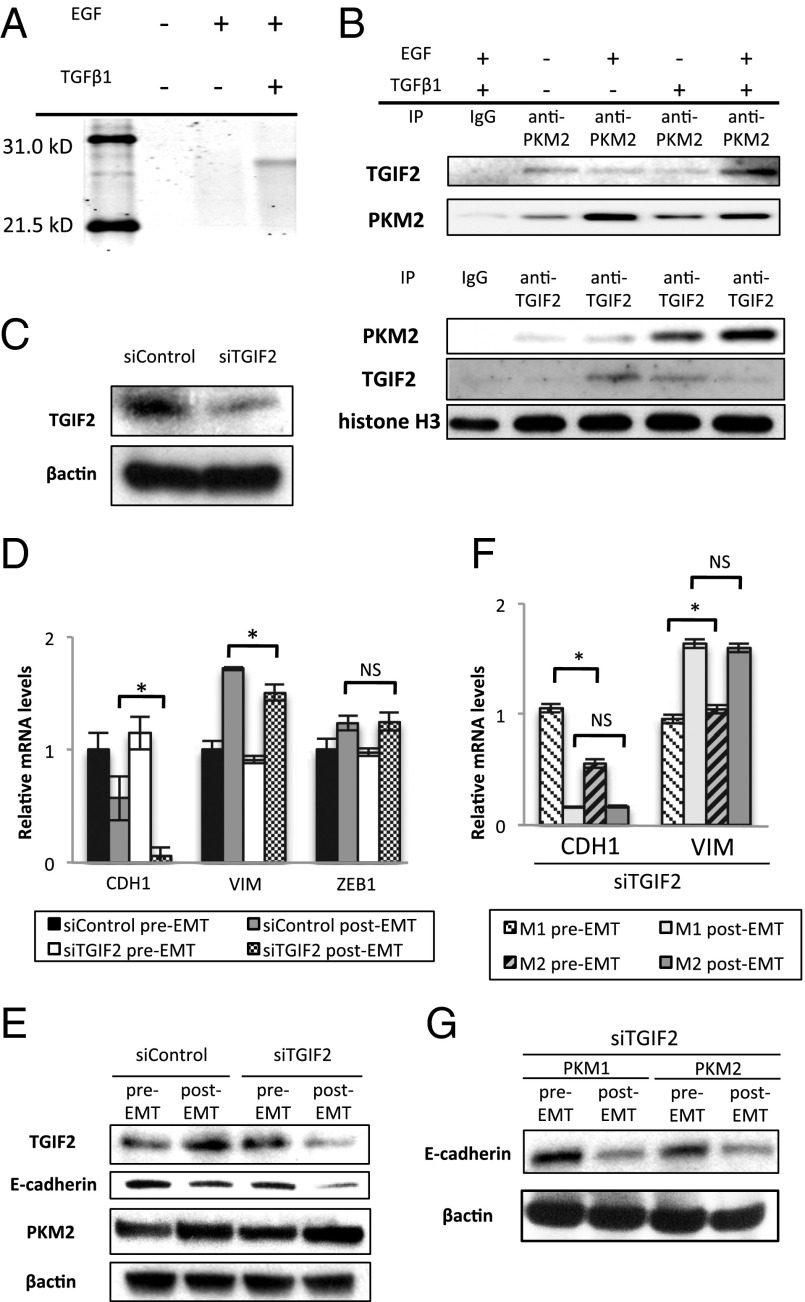
Fig. 3.
Interaction between nuclear PKM2 and TGIF2 mediates EMT induction. (A) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins immunoprecipitated with anti-PKM2 antibody in the nucleic lysate of cells cultured under normal conditions, with EGF alone, or with TGF-β1 and EGF. The band detected in samples of cells stimulated with TGF-β1 and EGF was excised and analyzed by MS. (B) Western blot assays of immunoprecipitated samples of nucleic lysates with anti-PKM2 or anti-TGIF2 antibody. Samples were harvested after the cells were treated as indicated for 72 h. (C) Western blot assays of TGIF2 and β-actin expression in cells transfected with siControl or siTGIF2. (D) Relative transcript (mRNA) levels of CDH1, VIM, and ZEB1 after induction of EMT in cells transfected with siControl or siTGIF2 for 72 h. (E) Western blot analysis of TGIF2, E-cadherin, PKM2, and β-actin expression in pre-EMT and post-EMT cells transfected with siControl or siTGIF2. Post-EMT samples were harvested at 72 h, when siRNA inhibition was profound. (F) Relative mRNA levels of CDH1 and VIM after EMT induction in PKM1 OE and PKM2 OE cells. Post-EMT samples were harvested at 72 h. (G) Western blot analysis of E-cadherin and β-actin after EMT induction in PKM1 OE and PKM2 OE cells transfected with siTGIF2. Post-EMT samples were harvested at 72 h. Column values = average of at least three independent experiments; error bars represent SD from the mean of triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05.