Figure 2.
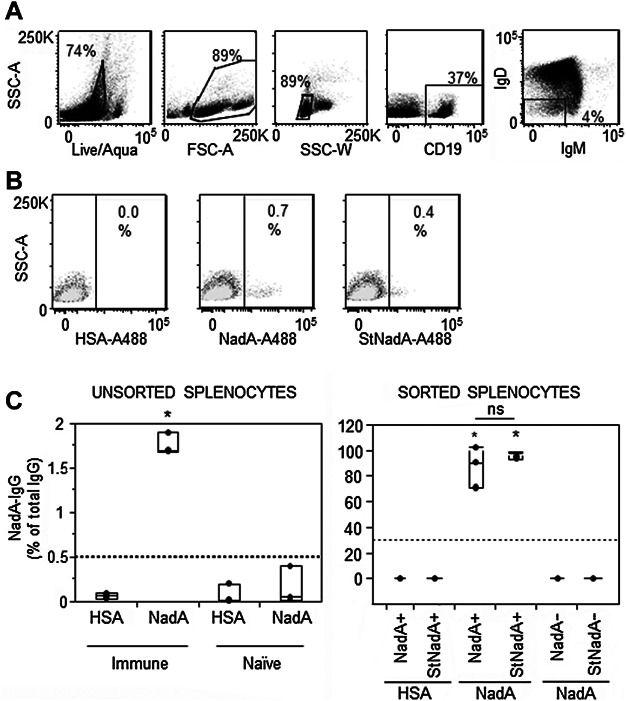
NadA-specific Ig-switched memory B cells are identifiable by FACS using amine-labeled and sortagged NadA-A488. (A) Murine splenocytes were gated based on Acqua live/dead staining, FSC × SSC morphology, single cells and CD19+IgD−IgM− to identify Ig-switched memory B cells. (B) NadA-specific Ig-switched memory B cells were identified by single antigen staining using amine-labeled (NadA-A488) and sortagged (stNadA-A488) NadA, with gating based on staining in naïve mice (overlay in light gray) and HSA-A488 specificity controls. Data are representative of one of three different experiments. (C) NadA-A488+ and StNadA-A488+ were sorted together with NadA− memory B cells and were cultured with CD19− cells sorted from the same samples. NadA-specific IgG secreted by the NadA-specific memory B cells were determined by ELISpot, after five days of in vitro polyclonal stimulation with CpG-2006 and IL-2. Shown are mean percentages of NadA-specific IgG+ antibody secreting cells among total IgG+ antibody secreting cells in cultures of unsorted immune and naïve splenocytes (left), or in cultures of NadA+, NadA−, StNadA+ or StNadA−IgD−IgM− cells sorted from immune mice (right). Results are from three independent experiments performed with splenocytes pooled from four mice per group in each experiment. Box plots represent median values and ranges. The asterisks indicate samples with significantly greater frequencies of NadA-specific IgG as compared to all the others (P-value <0.05 by the Tukey–Kramer test; ns: not statistically significant).
