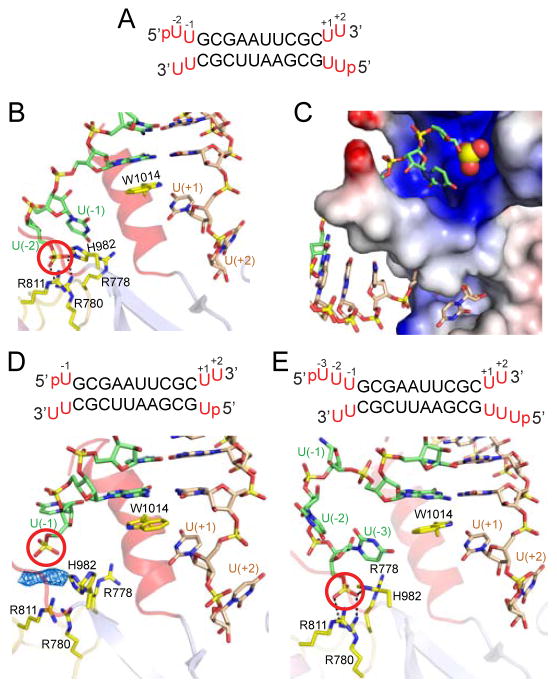
Figure 5. Structural Details of hDicer PAZ Cassette Bound to RNAs containing pUU (14-mer), pU (13-mer) and pUUU (15-mer) Overhangs at 5′-ends and UU Overhangs at 3′-ends.
(A) Sequence of the self-complementary 14-mer RNA containing pUU and UU-overhangs at 5′ and 3′-ends, respectively.
(B) A view of the positioning of the p-U(−1)-U(−2) at the 5′-end (green) and U(+1)-U(+2) at the 3′-end (wheat) on either side of the ‘hDicer-specific helix’ in the complex. Note that the 5′-phosphate (red circle) is positioned in the phosphate pocket and forms hydrogen bonds with basic residues. The base at position U(−2) is disordered.
(C) An expanded view of the phosphate and 3′-pockets in the 14-mer RNA complex, with the protein represented in an electrostatic surface representation. Note that the ‘hDicer-specific helix’ separates the basic phosphate pocket (above) from the hydrophobic 3′-overhang-binding pocket (below). The base at position U(−2) is disordered.
(D) Sequence of the 13-mer RNA duplex containing pU overhangs at 5′-ends and UU-overhangs at 3′-ends. A view of the positioning of the p-U(−1) at 5′-end (green) and U(+1)-U(+2) at 3′-end (wheat) on either side of the ‘hDicer-specific helix’ in the complex. The 5′-phosphate does not reach into the phosphate pocket that is represented by cluster of His and Arg residues. Unaccounted electron density is shown in a blue mesh representation, which could have originated from an additive used to facilitate crystallization.
(E) Sequence of the 15-mer RNA duplex containing pUUU overhangs at 5′-ends and UU-overhangs at 3′-ends. A view of the positioning of the p-U(−1)-U(−2)-U(−3) at 5′-end (green) and U(+1)-U(+2) at 3′-end (wheat) on either side of the ‘hDicer-specific helix’ in the complex. The base at position U(−1) is disordered. Intermolecular hydrogen-bonds are observed between the 5′-phosphate and the side chains of His982 and Arg780, with the side chains of Arg788 and Arg911 contributing to the basic nature of the phosphate-binding pocket in the complex.
See also Figure S7 and Table S2 and S3.