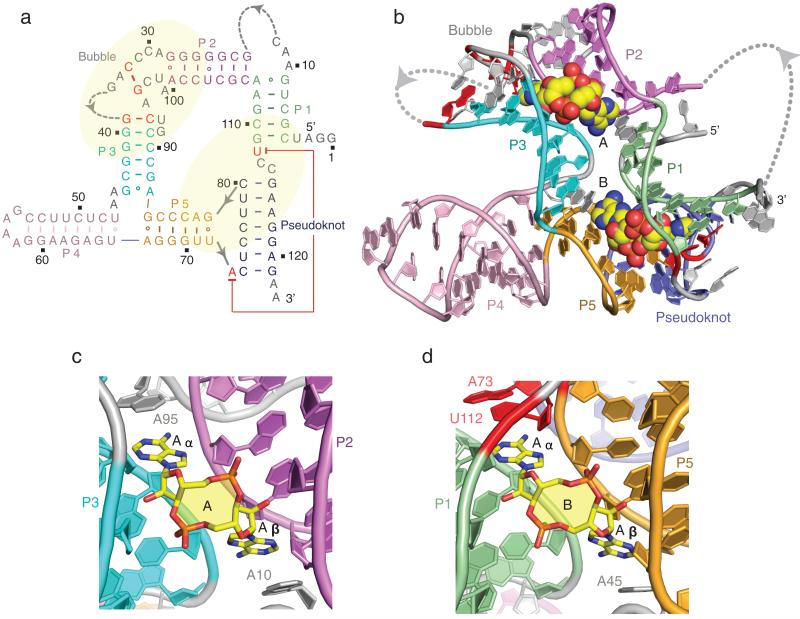
Figure 1. Secondary and tertiary structure of the T. tengcongensis ydaO riboswitch bound to c-di-AMP and alignment of c-di-AMP molecules A and B in their respective binding pockets.
a, The secondary fold of the sensing domain of the ydaO riboswitch. The stem segments are color-coded and labeled from P1 to P5, with additional labels marking segments containing a partially zippered-up bubble and a pseudoknot. The two c-di-AMP binding pockets identified from the crystal structure of the complex are marked in yellow background. b, The 2.73 Å crystal structure of the sensing domain of the ydaO riboswitch with two bound c-di-AMP molecules labeled A and B in space-filling representation. c, c-di-AMP molecule A (in yellow) bound within its pocket composed of stems P2 (in purple) and P3 (in cyan) and bubble (in grey) segments in the ydaO riboswitch complex. d, c-di-AMP molecule B (in yellow) bound within its pocket composed of stems P1 (in green) and P5 (in orange) and pseudoknot duplex (in blue) segments.