Abstract
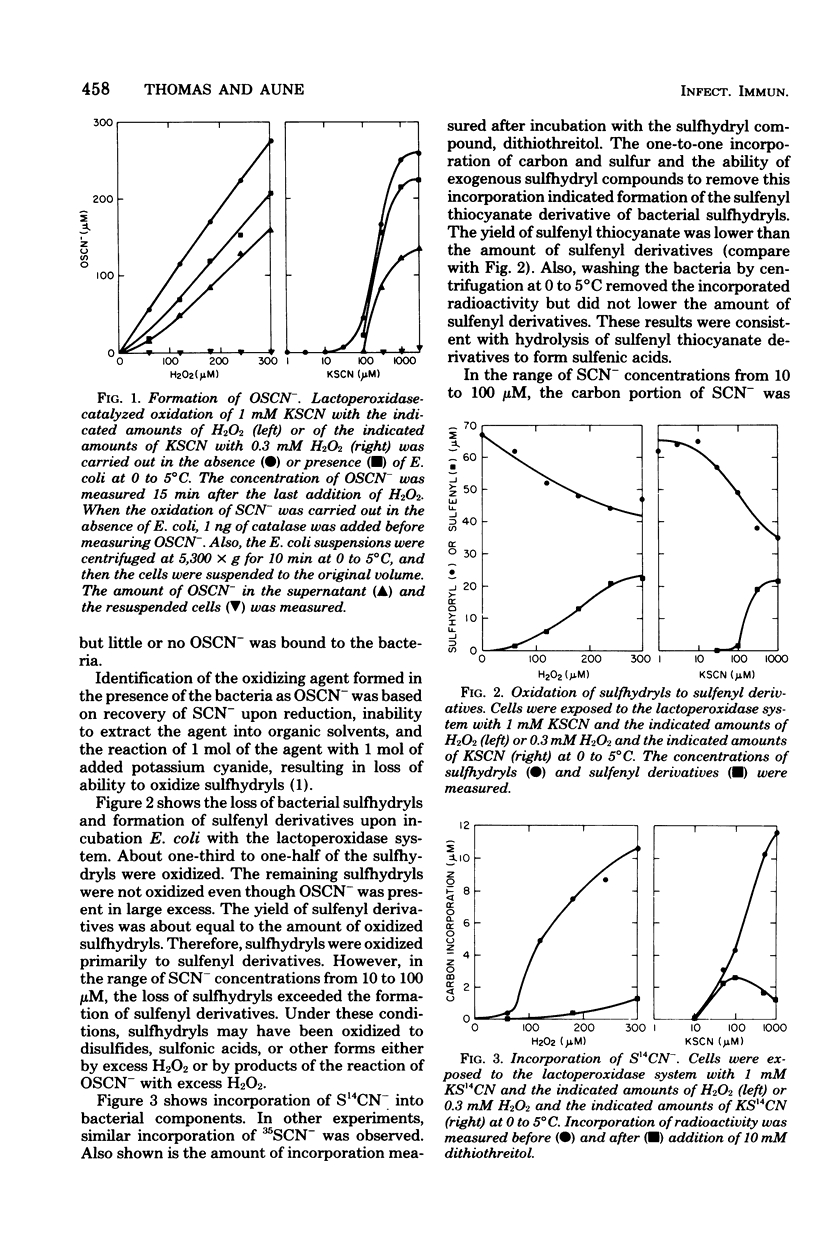
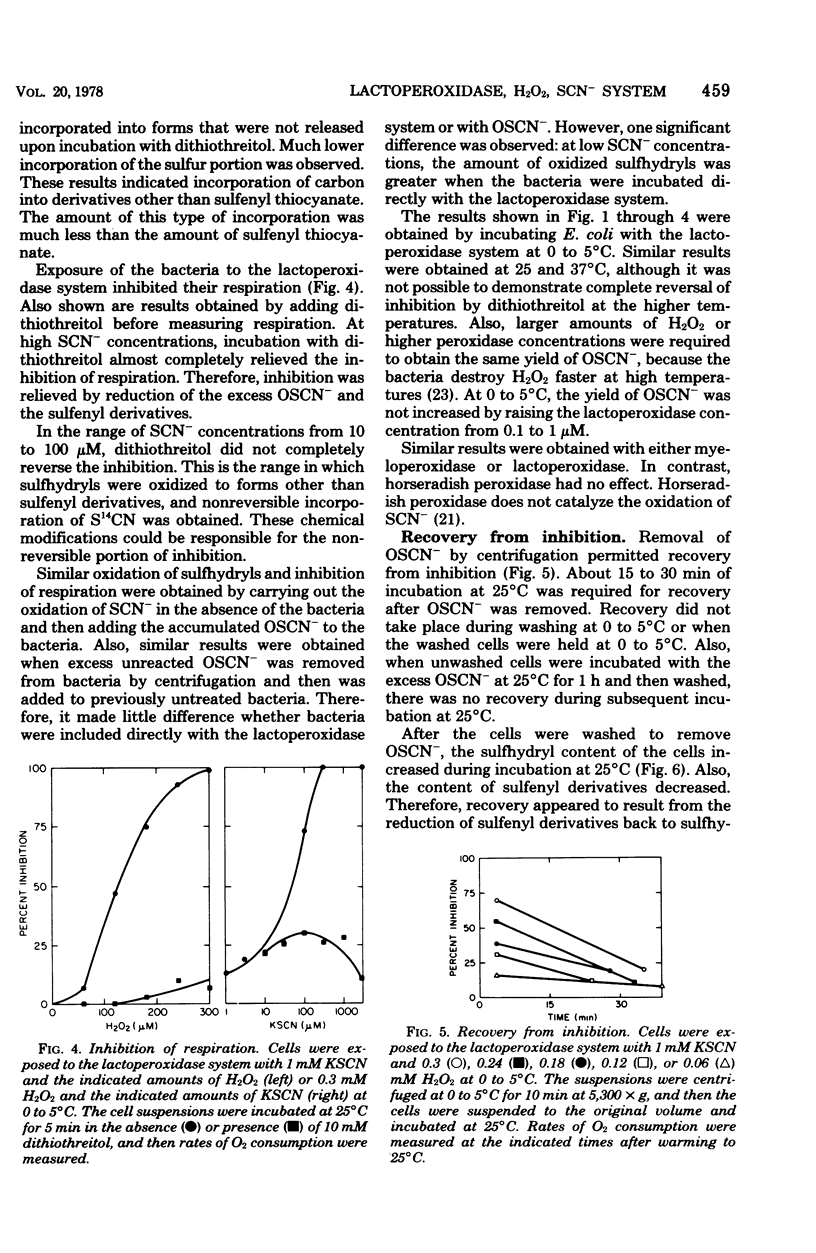
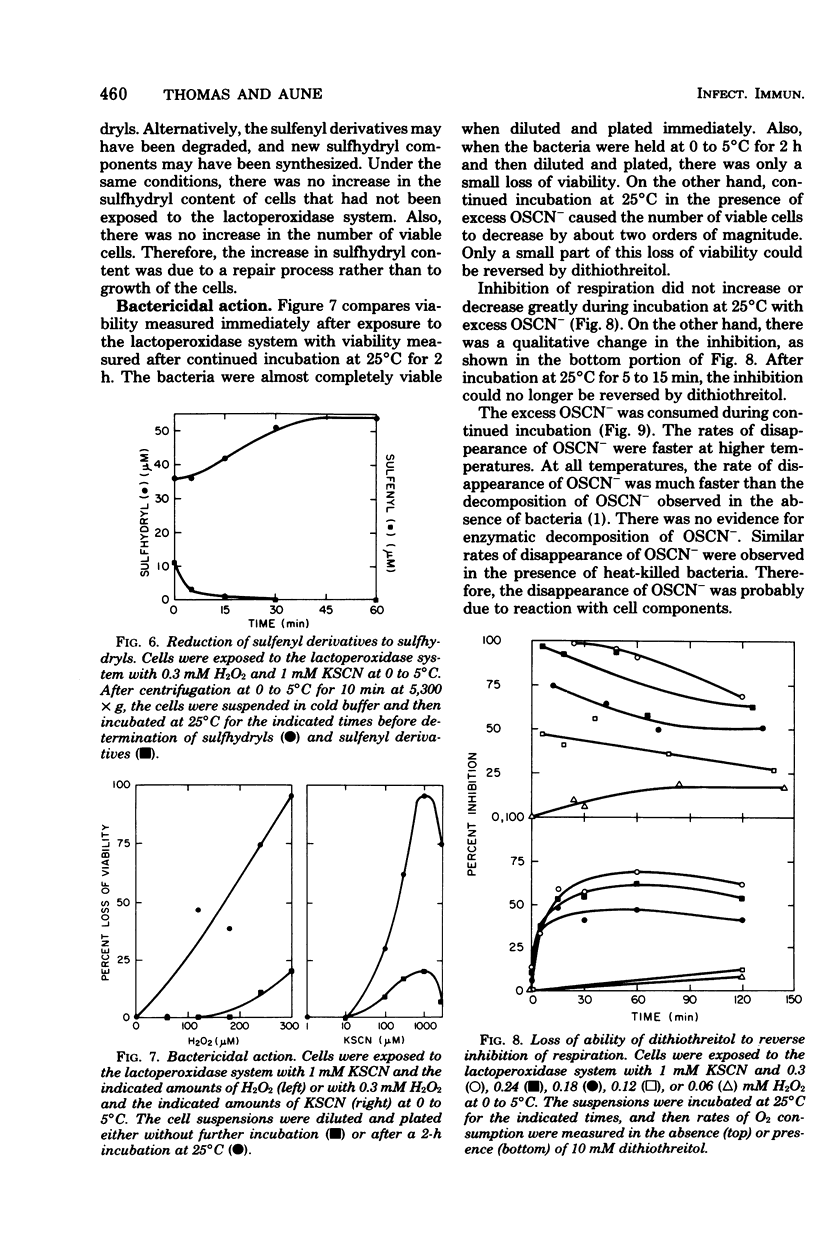
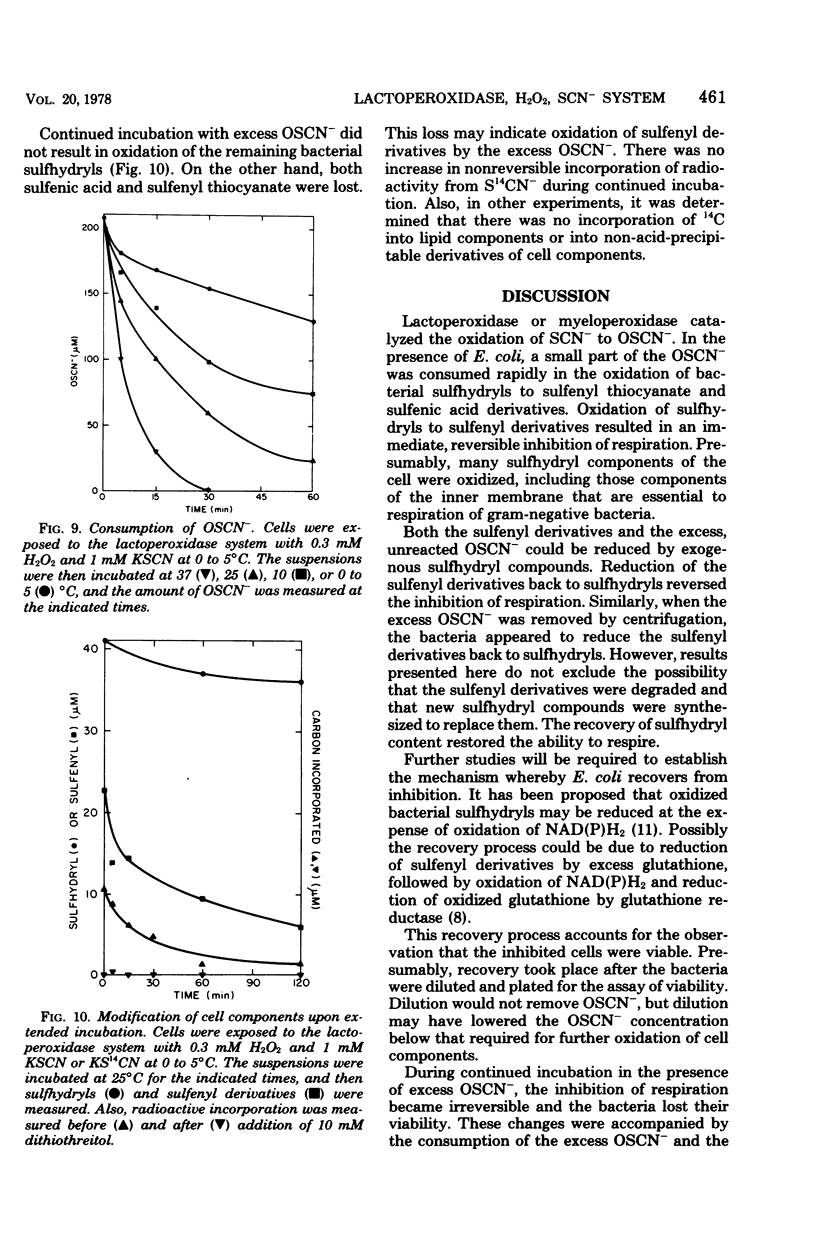
The antimicrobial activity of the lactoperoxidase, peroxide, thiocyanate system against Escherichia coli was directly related to the oxidation of bacterial sulfhydryls. Lactoperoxidase catalyzed the oxidation of thiocyanate, which resulted in the accumulation of hypothiocyanite ion, OSCN-. A portion of the bacterial sulfhydryls were oxidized by OSCN- to yield sulfenic acid and sulfenyl thiocyanate derivatives. The remaining sulfhydryls were not oxidized, although OSCN- was present in large excess. The oxidation of sulfhydryls to sulfenyl derivatives inhibited bacterial respiration. This inhibition could be reversed by adding sulfhydryl compounds to reduce the sulfenyl derivatives and the excess OSCN-. Also, this inhibition could be reversed by washing the cells so as to remove the excess unreacted OSCN-. After washing, the bacteria underwent a time-dependent recovery of their sulfhydryl content. This recovery resulted in recovery of the ability to respire. The inhibited cells were viable if diluted and plated shortly after the incubation with the lactoperoxidase, peroxide, thiocyanate system. On the other hand, long-term incubation in the presence of the excess OSCN- resulted in loss of viability. Also, the inhibition of respiration became irreversible. During this long-term incubation, the excess OSCN- was consumed and the sulfenyl derivatives disappeared.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aune T. M., Thomas E. L. Accumulation of hypothiocyanite ion during peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of thiocyanate ion. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aune T. M., Thomas E. L., Morrison M. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed incorporation of thiocyanate ion into a protein substrate. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4611–4615. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Rosén C., Marshall V., Reiter B. Antibacterial activity of the lactoperoxidase system in milk against pseudomonads and other gram-negative bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):199–204. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.199-204.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon C. B., Klebanoff S. J. A peroxidase-mediated, streptococcus mitis-dependent antimicrobial system in saliva. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):438–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg D. M., Jago G. R. The antibacterial action of lactoperoxidase. The nature of the bacterial inhibitor. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):779–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1170779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogendoorn H., Piessens J. P., Scholtes W., Stoddard L. A. Hypothiocyanite ion; the inhibitor formed by the system lactoperoxidase-thiocyanate-hydrogen peroxide. I. Identification of the inhibiting compound. Caries Res. 1977;11(2):77–84. doi: 10.1159/000260252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGO G. R., MORRISON M. Anti-streptococcal activity of lactoperoxidase III. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:585–588. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON M., HULTQUIST D. E. LACTOPEROXIDASE. II. ISOLATION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2843–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson M. N. Effect of lactoperoxidase and thiocyanate on the growth of Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae in a chemically defined culture medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Apr;43(1):31–43. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Reiter B. The inhibition of streptococci by lactoperoxidase, thiocyanate and hydrogen peroxide. The effect of the inhibitory system on susceptible and resistant strains of group N streptococci. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):373–381. doi: 10.1042/bj1000373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Reiter B. The inhibition of streptococci by lactoperoxidase, thiocyanate and hydrogen peroxide. The oxidation of thiocyanate and the nature of the inhibitory compound. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):382–388. doi: 10.1042/bj1000382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. J., Allison W. S. The mechanism of inactivation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase by tetrathionate, o-iodosobenzoate, and iodine monochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter B., Marshall V. M., BjörckL, Rosén C. G. Nonspecific bactericidal activity of the lactoperoxidases-thiocyanate-hydrogen peroxide system of milk against Escherichia coli and some gram-negative pathogens. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):800–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.800-807.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele W. F., Morrison M. Antistreptococcal activity of lactoperoxidase. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.635-639.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Aune T. M. Susceptibility of Escherichia coli to bactericidal action of lactoperoxidase, peroxide, and iodide or thiocyanate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELDOW B. J. Studies on the antibacterial action of human saliva. III. Cofactor requirements of Lactobacillus bactericidin. J Immunol. 1963 Jan;90:12–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


