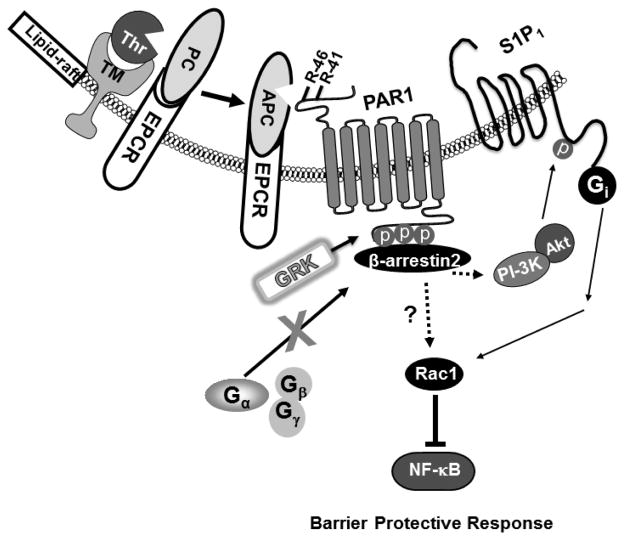
Fig. 1.
Cartoons of protein C activation and APC signaling in the membrane lipid-rafts of endothelial cells. Thrombin binds to thrombomodulin and activates the EPCR-bound protein C zymogen to APC in the membrane lipid-rafts of endothelial cells. APC, remained associated with EPCR, activates PAR1 through the cleavage of Arg-41 and/or Arg-46 on the extracellular domain of the receptor. The activation of PAR1 by APC results in a conformational change on the C-terminal intracellular loop of the receptor, thereby mediating its phosphorylation by a member of G protein coupled receptor kinases (GRK). The phosphorylated receptor recruits β-arrestin2, thereby preventing the interaction of the receptor with α subunit of one of the heterotrimeric G proteins and transmitting the intracellular message via β-arrestin2 biased signaling mechanism. This mode of activation of PAR1 by APC results in the activation of the PI-3K/Akt survival pathway, transactivation of the Gi protein coupled receptor, S1P1 and activation of Rac1 GTPase. These signaling events lead to improvement in the barrier permeability function and inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in endothelial cells.