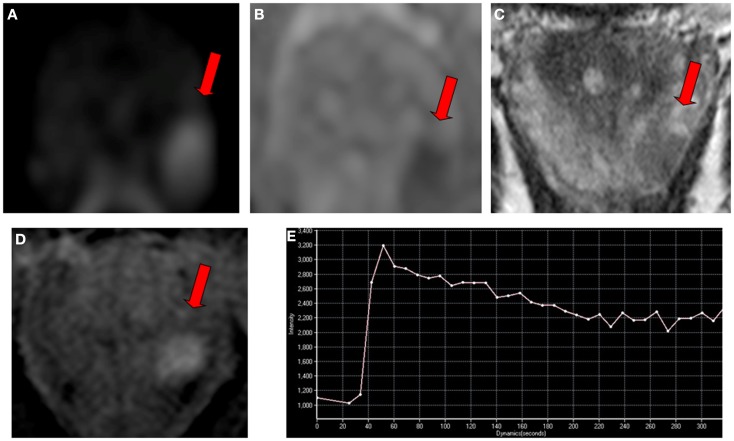
Figure 1.
Multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging in a 65-year-old man referred for early detection of prostate cancer with an elevated serum PSA level (7 ng/ml) and a normal digital rectal examination. Magnetic resonance imaging consisted of conventional T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted, and dynamic contrast-enhanced sequences performed on a 3 T unit without endorectal coil. (A) An ovoidal hyperintense lesion (arrow) was observed on axial diffusion-weighted imaging at b-value 1000 s/mm2 in left apical peripheral zone. (B) The lesion (arrow) corresponded to hypointense lesion on apparent diffusion coefficient map. (C) The lesion (arrow) also corresponded to axial T2-weighted image with low signal intensity, and to (D) focal enhanced lesion on axial dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging with a type 3 enhancement curve (washout) (E). The final Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System score for this lesion was four. The presence of a clinically significant cancer was confirmed with a targeted biopsy, showing an 8-mm Gleason score 4 + 3 adenocarcinoma.