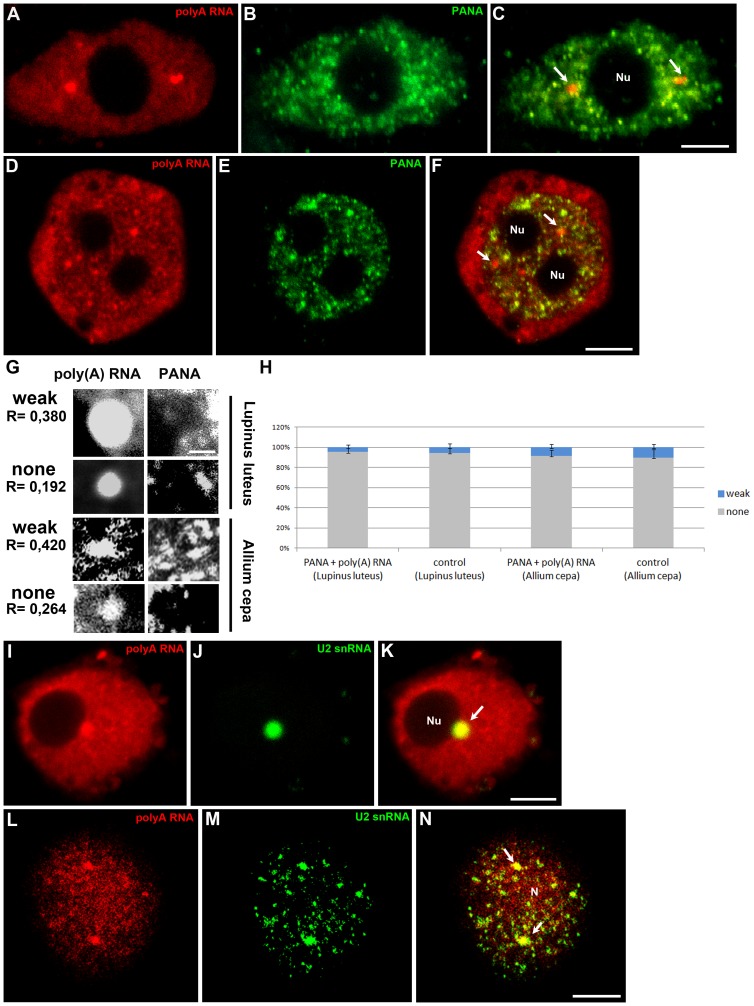
Figure 2. Double labelling of poly(A) RNA and the PANA antigen in the chromocentric (Lupinus) (A–C) and reticular (Allium) (D–F) nuclei of root cells.
In the nucleoplasm of both species, poly(A) RNA is present in nuclear structures (arrows) and does not colocalise with speckles. Representative examples of Pearson correlation coefficients for weak and non-colocalisation of poly(A) mRNA with the PANA antigen in Lupinus luteus and Allium cepa cells (G). A scale bar representing 2 µm is shown. The percentages of weak and non-colocalisation of poly(A) RNA-rich bodies with the PANA antigen are indicated by the Pearson correlation coefficient (H). Error bars represent standard error. Double labelling of poly(A) RNA and U2 snRNA in Lupinus (I–K) and Allium (L–N) cells. Accumulation of poly(A) RNA in nuclear bodies rich in U2 snRNA (arrows). Bar, 5 µm. N-nucleus, Nu- nucleolus