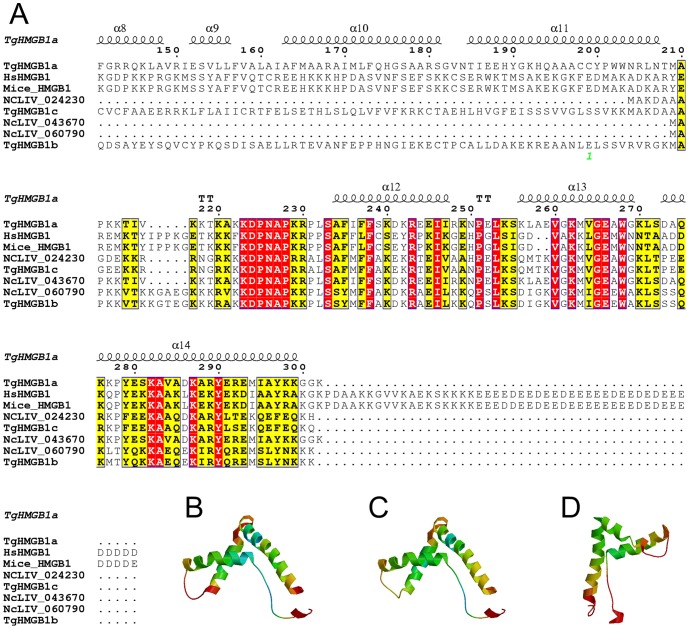
Figure 1. Sequence-structure alignment of HMGB1s and spatial structures prediction of HMG box in TgHMGB1a, b and c.
A. T. gondii and N. caninum HMG box domains were identified using Motif Scan and are marked by a box and compared with sequences of human and mice. The positions of identical and conserved residues contained in the HMG box are indicated by red- and yellow-filled rectangular frames, respectively. Dots indicate gaps or missing residues. The secondary structure of TgHMGB1a was also predicted and α-helices 12, 13 and 14 represent the three α-helices of the TgHMGB1a HMG box. B, C, and D. A three-dimensional model of the HMG box in TgHMGB1a (B), TgHMGB1b (C) and TgHMGB1c (D) were built based on homology modeling. As shown here, the three α-helices fold into a characteristic L-shaped domain expected for a HMG box.