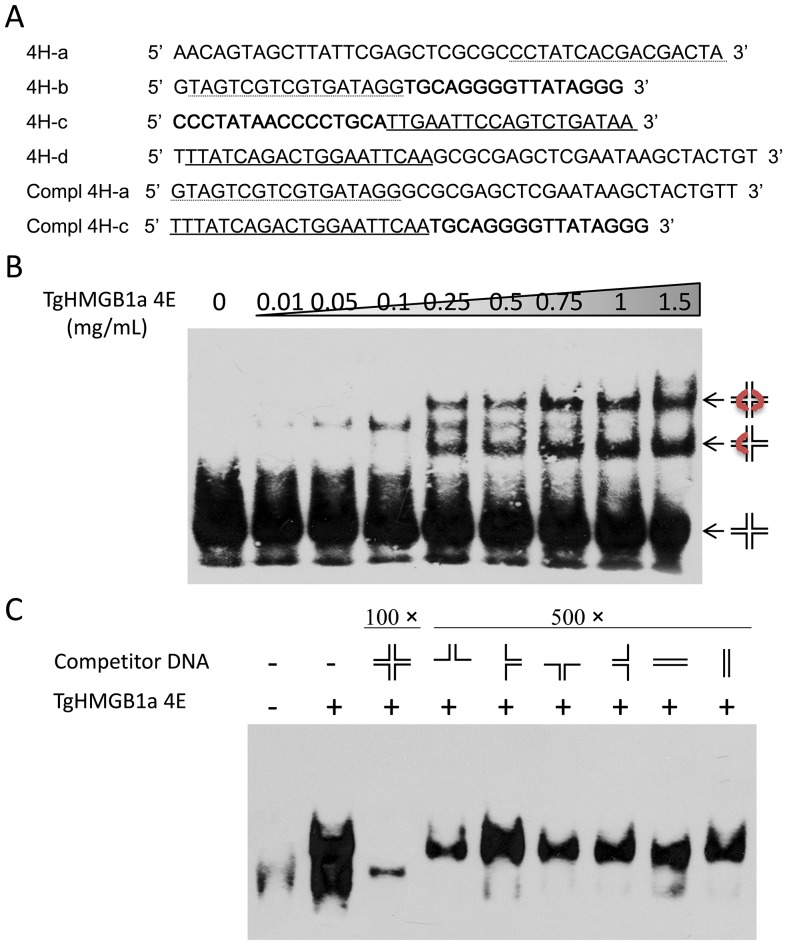
Figure 4. TgHMGB1a binds to cruciform DNA.
A. Oligonucleotides used to form the different synthetic DNA structures. Identical text formats (italic, bold, dotted/solid underlines) represent complementary sequences. All of the primers were labeled using EMSA Probe Biotin Labeling Kit as described in methods. Cruciform 4H structures were obtained by annealing equal amounts of 4H-a, -b, -c and -d primers; 2H hairpin-like structures, by annealing of 4H-a and -b, -b and -c, -c and -d, -d and -a, respectively; double stranded (ds) linear DNA structures were obtained by annealing of 4H-a or 4H-c with its fully complementary sequence (compl 4H-a and compl 4H-c). B. EMSA with cruciform DNA (4H) and recombinant TgHMGB1a 4E. Increasing concentrations of TgHMGB1a 4E protein (0.01–1.5 mg/mL) were incubated with biotinlabeled 4H DNA for 30 min at 25°C. DNA–protein complexes formed were resolved on 6% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel and transferred to nylon membrane and then detected by Chemiluminescent EMSA Kit. Lane 1, free labeled 4H; lanes 2–8, 4H DNA–protein complexes formed with increasing concentrations of TgHMGB1a 4E. C. Competition EMSA experiments were performed with different cold DNA structures. After incubation of TgHMGB1a 4E (1 mg/mL) with biotinlabeled 4H, cold complete 4H (in a 100-fold excess), hairpin-like 2H structures (in a 500- fold excess) or ds linear DNA (in a 500-fold excess) were added, and incubated for an additional 20 min. Complex formation was analyzed as in B. Lane 1, free labeled 4H; lane 2, 4H DNA–protein complexes formed with TgHMGB1a 4E without competitor DNA; lane 3, competition assay with 100-fold excess cold 4H; lanes 4–7 competition assay with 500-fold excess cold 2H hairpin-like structures; lanes 8–9, competition assay with 500-fold excess cold linear ds DNA.