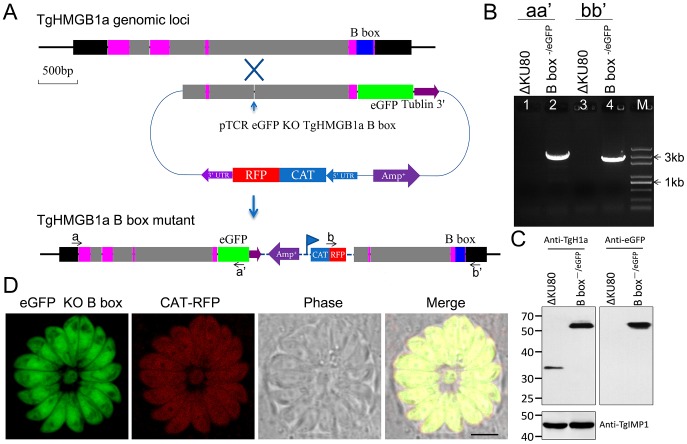
Figure 5. Generation of a TgHMGB1a B box mutant strain.
A. Schematic of the experimental design. TgHMGB1a is encoded by 4 exons, and the B box is located in the fourth exon (shown for the TgHMGB1a genomic locus). An “O-type” knock-in/knock-out vector (pTCR eGFP KO TgHMGB1a B box) was constructed to target and replace the B box domain. The vector included an approximately 2200 bp homologous arm upstream of the TgHMGB1a B box, and a monoclonal site of restriction endonuclease (BsiWI) throughout the whole vector sequence was not only needed, but also necessary in the homologous arm, and it is was best ranged around the middle of homologous frame [55]. If the targeted gene was successfully disrupted, eGFP should replace the TgHMGB1a B box domain and create a fusion protein of TgHMGB1a B box−/eGFP expressed under the control of its endogenous promoter. CAT-RFP was used as a selection marker. B. Genomic PCR analysis of the ΔKU80-TgHMGB1a B box−/eGFP strain. The position of the primers and the expected sizes are shown in panel A. C. Western blot performed with anti-TgHMGB1a 4E antibodies on total extracts from RHΔKU80 and ΔKU80-TgHMGB1a B box−/eGFP strains. TgIMP1 was used as an internal control. D. Observation of the TgHMGB1a B box−/eGFP and CAT-RFP strains by fluorescent confocal microscopy, and the result indicated that B box mutant TgHMGB1a was dispersed throughout the parasite cells. Scale bar, 3 µm.