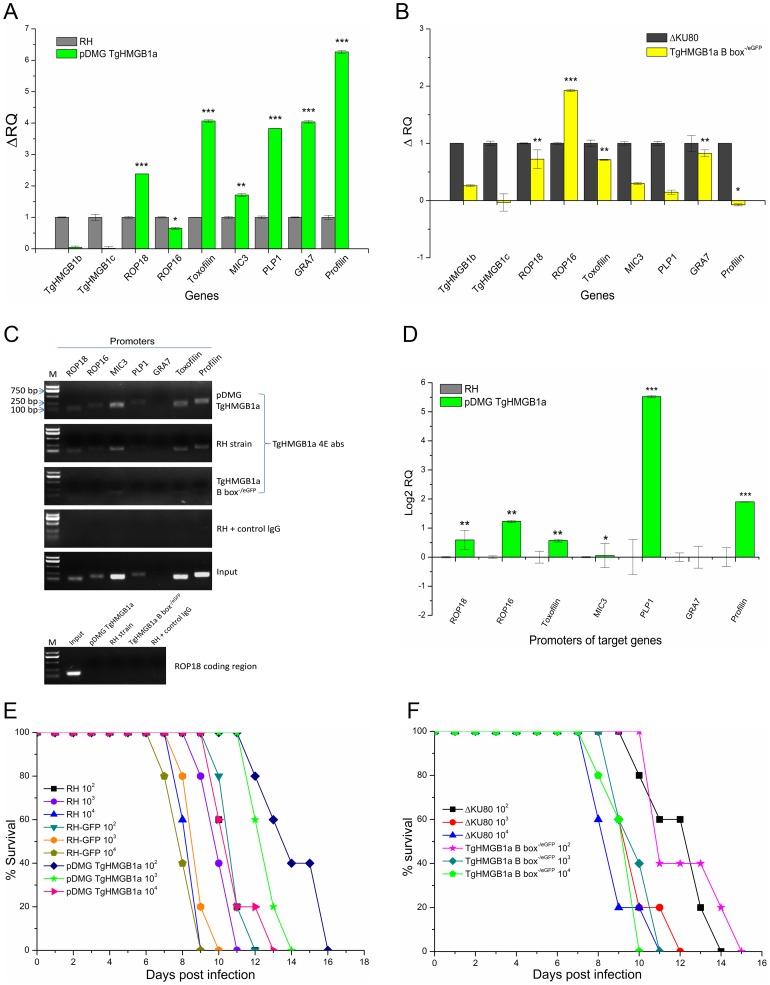
Figure 7. TgHMGB1a involves to gene transcription regulatory and overexpress but not disrupt TgHMGB1a can delayed the death of mice.
A and B. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to analyze the transcription levels of the indicated genes in TgHMGB1a overexpression (A) and B box-deficient (B) parasites compared with their parental strains. Each bar indicates the relative quantity (RQ) ± SD. RQs of the transgenic parasites were calibrated using their parental strains (i.e., ΔRQtransgenic parasite = RQtransgenic parasite – RQparental strain( = 1)). Data presented are representative of three independent experiments, each done in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined using Student's t-test (*P<0.1, **P<0.05, ***P<0.005). C and D. Analysis of TgHMGB1a binds to promoters of indicated genes through chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). C. Regular PCR was performed on the ChIP DNAs from the TgHMGB1a overexpress and RH strains using the promoter-specific primers of indicated genes, normal mice sera, input DNA and TgHMGB1a B box−/eGFP strain were used as ChIP controls, ROP18 coding region was also tested as negative control. PCR products were run on 1.5% agarose gels. D. Quantitative real-time PCR was carried out and the pull-down promoters in RH and TgHMGB1a overexpress strains were normalized against the corresponding input DNA, the promoters level in TgHMGB1a overexpress parasites were represented as log2 functions of relative ratios to RH strain. Data presented are representative of three independent experiments, each done in triplicate. Analysis was carried out using Student's t-test. *P<0.1, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. E and F. Mouse survival curves for parental and TgHMGB1a transgenic lines. Balb/c mice were separately injected i.p. with the indicated parasites and doses. Mean values shown per group (n = 5), representative of 3 experiments with similar outcomes. Mice infected with the TgHMGB1a overexpression showed a significantly delayed time to death (3 to 5 days) in a low doses (102 and 103) infection compared to its parental RH or RH-GFP strains (P<0.0001 was considered as statistically significant difference, see the Data S1).