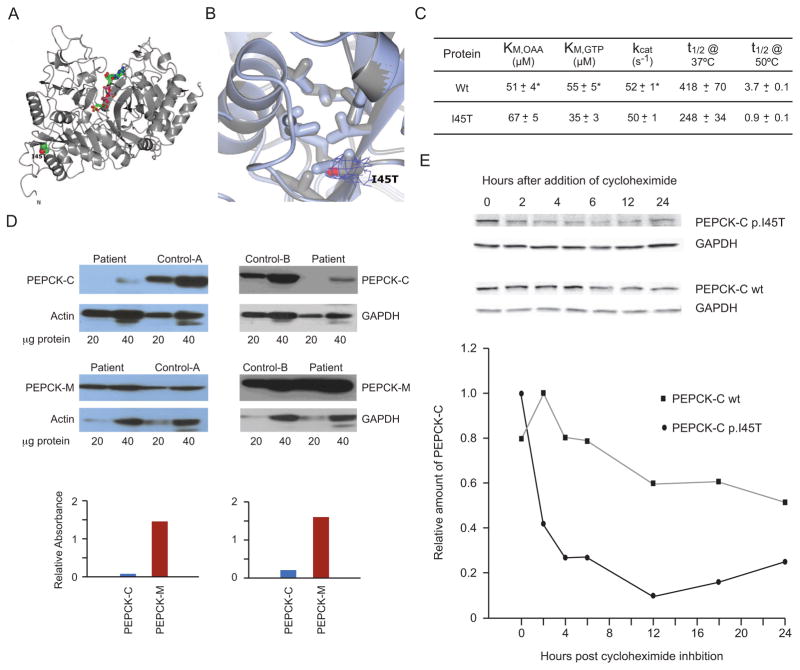
Fig. 3.
Structural and Functional Properties of the Mutant PEPCK-C. (A) The overall structure of crystallized recombinant I45T PEPCK-C indicating the location of the I45T mutation with respect to the overall enzyme structure and the active site (indicated by the molecules of βSP and GTP rendered as ball and stick models colored by atom type). The N- and C-termini are also labeled. (B) The comparison of WT (light blue, PDB 3DT7) and I45T PEPCK-C (grey, PDB 4OX2, this work) in the vicinity of I45 illustrates that the local structure of the hydrophobic pocket is not perturbed upon the threonine for isoleucine substitution. 2Fo-Fc density corresponding to the side-chain of T45 is illustrated as a blue mesh rendered at 1.2 σ. (C) Kinetic characterization of recombinant I45T PEPCK-C compared with the wild type (WT) enzyme, showing very similar kinetic parameters (KM for both OAA and GTP and kcat), and heat stability (t1/2) at two temperatures (*WT data is from [20]). (D) Western blots of PEPCK-C and PEPCK-M in frozen liver from patient 1 and two controls. Figures above show western blots specific for PEPCK-C and PEPCK-M and the reference proteins β-actin or GAPDH, with the amount of micrograms of protein homogenate beneath, for patient 1 and human controls A or B. Graphs below these respective blots comparing the normalized signal intensity (corrected for the ratio to their reference proteins) of ratios of PEPCK-C (blue) and PEPCK-M (red) in the patient vs controls A and B. (E) Half lives of mutant I45T and wt PEPCK-C in T-Rex 293 cultured stable inducible cell lines. Figure above shows Western blots at indicated time intervals before and after tetracycline induction of PEPCK-C I45T (upper row), PEPCK-C wt (lower row), and GAPDH as a reference protein. Graph below shows relative amounts of PEPCK-C I45T/GAPDH (solid circles) and PEPCK-C/GAPDH wt (solid squares) over 24 h after induction, to establish the mutant and wild type protein half-lives.