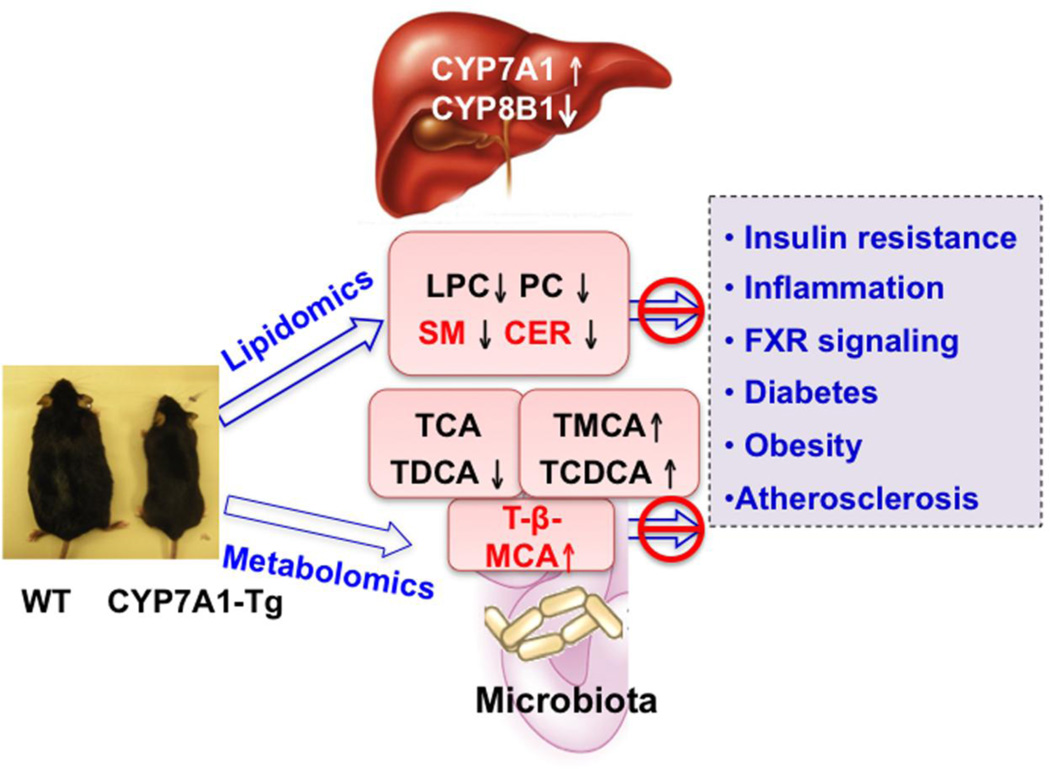
Fig 8. Mechanisms of anti-diabetic and anti-obesity function of bile acids in CYP7A1-tg mice.
In CYP7A1-tg mice, overexpressing CYP7A1 increases bile acid pool size and reduces cholic acid by inhibiting CYP8B1. Lipidomics analysis revealed decreased serum LPC, PC, SM and CER. These lipidomic markers are increased in hepatic steatosis and NAFLD. Bile acids may reduce LPC, PC, SM and CER levels and protect against high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity in CYP7A1-tg mice. Metabolomics analysis showed decreased intestinal TCA and TDCA and increased intestinal T-β-MCA In CYP7A1-tg mice. High fat diets are known to increase CA synthesis and intestinal inflammation. It is proposed that decreasing CA and DCA synthesis may increase intestinal T-β-MCA, which antagonizes FXR signaling to increase bile acid synthesis and prevent high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity.