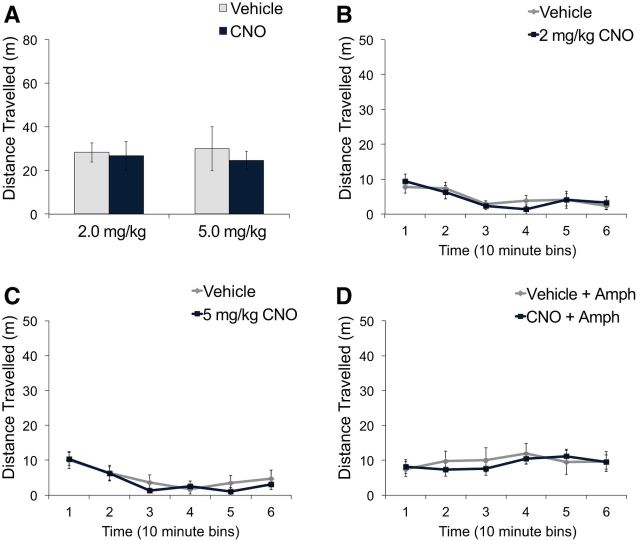
Figure 2.
hM4D-mediated inhibition of vHPC PV neurons did not affect spontaneous or amphetamine-induced locomotor activity. PV-Cre mice expressing hM4D in PV neurons of the vHPC were administered vehicle or CNO intraperitoneally. A, CNO activation of hM4D did not significantly change total spontaneous locomotor activity after either 2 mg/kg CNO (n = 8) or 5 mg/kg CNO (n = 8) compared with vehicle treatment. There were no significant differences in distance traveled across 10 min bins between vehicle and 2 mg/kg CNO (B) or 5 mg/kg CNO (C). D, Amphetamine (1 mg/kg)-induced locomotor activity was not significantly different between CNO-treated (5 mg/kg, n = 10) and vehicle-treated mice (n = 10). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.