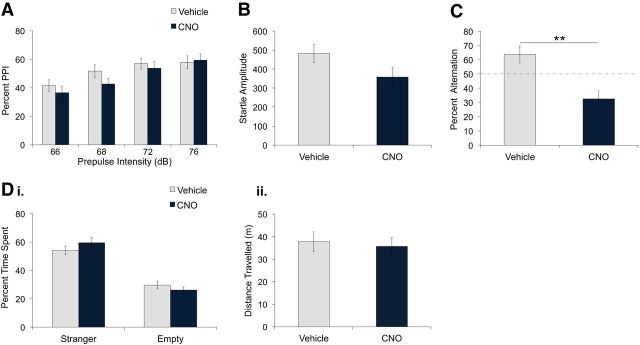
Figure 6.
hM4D-mediated inhibition of vHPC GAD65 neurons impaired spontaneous alternation but did not affect percentage PPI, startle amplitude, or social interaction. GAD65-Cre mice expressing hM4D in GAD65 neurons of the vHPC were administered vehicle or CNO intraperitoneally. A, B, No significant differences in percentage PPI (A) or startle amplitude (B) during pulse-alone trials were found between mice treated with CNO (5 mg/kg, n = 8) and vehicle (n = 7). C, CNO (0.5 mg/kg, n = 8) reduced percentage alternation compared with vehicle (n = 8). **p = 0.001. Di, Dii, In the social interaction test, percentage time spent in the stranger and empty chambers (i) and distance traveled (ii) were not significantly different between vehicle and CNO treatment (0.5 mg/kg, n = 8). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.