Figure 10.
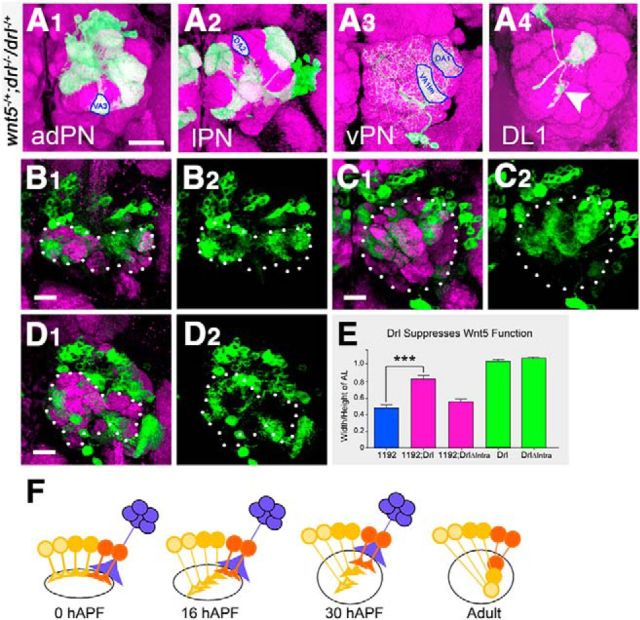
Drl antagonizes the repulsive function of Wnt5 in PN Dendrites. To assess genetic interaction between drl and wnt5, the MARCM technique was used to eliminate drl function in clones of PNs in the wnt5 heterozygous background. Adult ALs were stained with nc82 (magenta) and anti-CD8 (green) to visualize the neuropil and PN clones; merged images are shown. In the presence of half the dose of the wnt5 gene, drl mutant adPN, lPN, and vPN dendrites exhibited wild-type patterns of targeting (A1–A3, compare with Fig. 8B1–B4). Blue circles indicate wild-type targeting of select dendrites. DL1 dendrites still showed slight defects (A4, arrowhead). Thus, a reduction in wnt5 function strongly suppressed the drl loss-of-function mutant phenotype. Adult ALs from animals expressing UAS-wnt51192 under the control of GH146-Gal4 (B–D) were stained with nc82 (magenta) and anti-CD8 (green). Merged channels are shown on the left and green channels are shown on the right. Dotted lines highlight the ALs. Expression of UAS-wnt51192 by the PNs resulted in severe distortion of the ALs, with the ALs acquiring an abnormal dumbbell shape (B1, B2). Coexpression of the UAS-drl transgene, encoding a full-length Drl protein, with UAS-wnt51192 strongly suppressed the wnt5 gain-of-function phenotype, restoring the AL to a more wild-type shape (C1, C2). Coexpression of the UAS-drlΔintra transgene, encoding a truncated Drl protein, with UAS-wnt51192 did not suppress the wnt5 gain-of-function phenotype (D1, D2). The effect of the overexpression of the wnt5 and drl genes on AL morphology and their genetic interactions is quantified in E. These genetic interaction data indicated that drl and wnt5 act antagonistically in PN dendritic migration. A model of how Wnt5 and Drl control PN dendritic migration is presented in F. PNs express different levels of Drl (red, orange, yellow), which allow their dendrites to differentially respond to the DL > VM Wnt5 gradient. The Wnt5 protein is deposited at the dorsolateral edge of the AL by DLC neurons (blue). PNs expressing high levels of Drl (red) are less repelled by Wnt5 and remain in the dorsolateral AL, whereas PNs expressing low levels of Drl (yellow) are strongly repelled by Wnt5 and migrate to the ventrolateral AL; ***p < 0.0001. Scale bar, 10 μm.