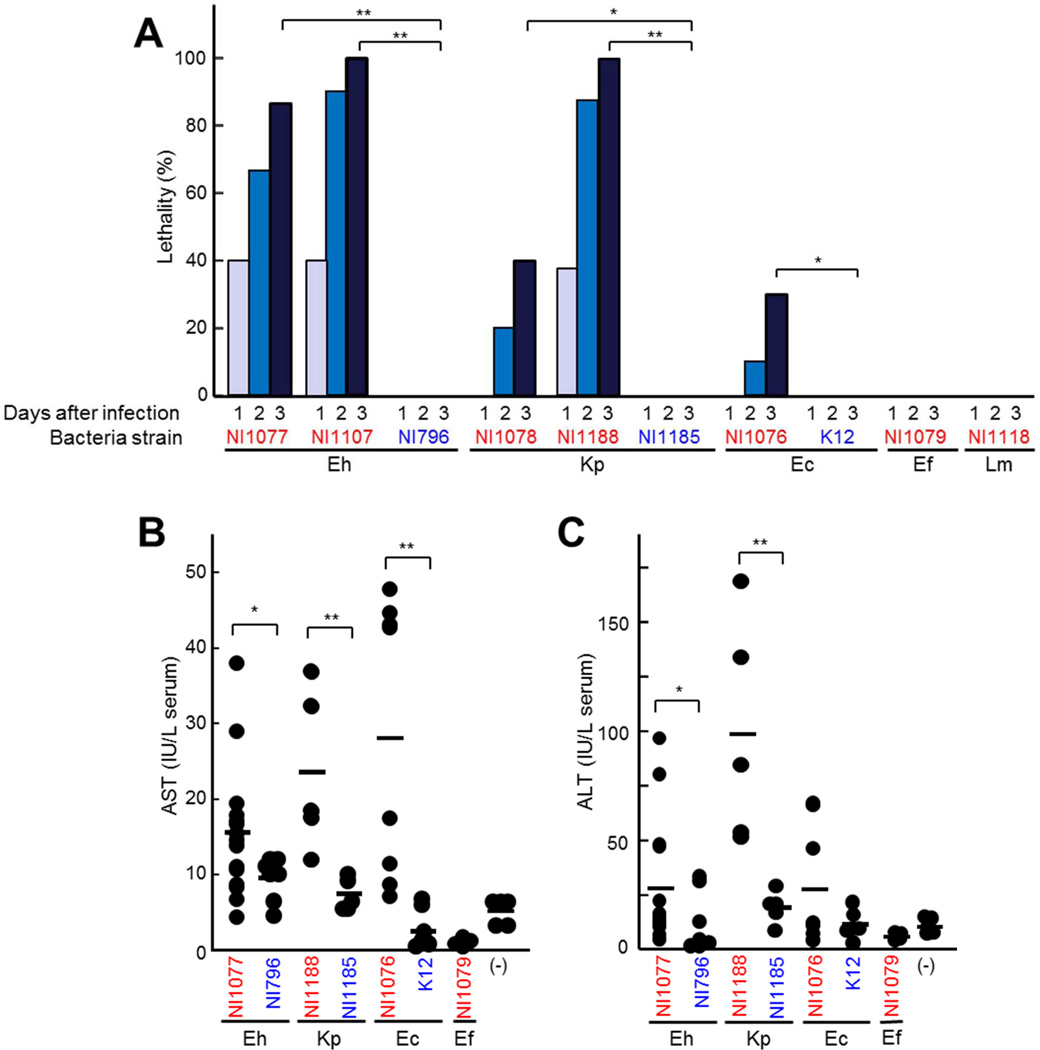
Figure 3. Enterobacteria isolated from liver of mice infected with C. difficile exhibit enhanced lethality after intravenous administration.
A to D, Enterobacteriaceae E. hormaechei (Eh) NI1077, NI1109, NI796; K. pneumoniae (Kp) NI1078, NI1188, NI1185; E. coli NI1076, K12; Lactobacillales E. faecalis (Ef) NI1079 and L. murinus (Lm) NI1118 were administered (2×108 CFU) to WT mice i.v.. A, Survival of infected mice (n=10) were monitored for 14 days. No additional deaths were observed beyond 5 days after infection. Results are representative of three independent experiments. B and C, The concentrations of AST (B) and ALT (C) in the serum 3 days after infection. Strains isolated from the liver after C. difficile infection are indicated in red, whereas control strains (isolates from the murine intestine and K-12) are indicated in blue. Bars indicate means. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. Results are representative of three independent experiments.