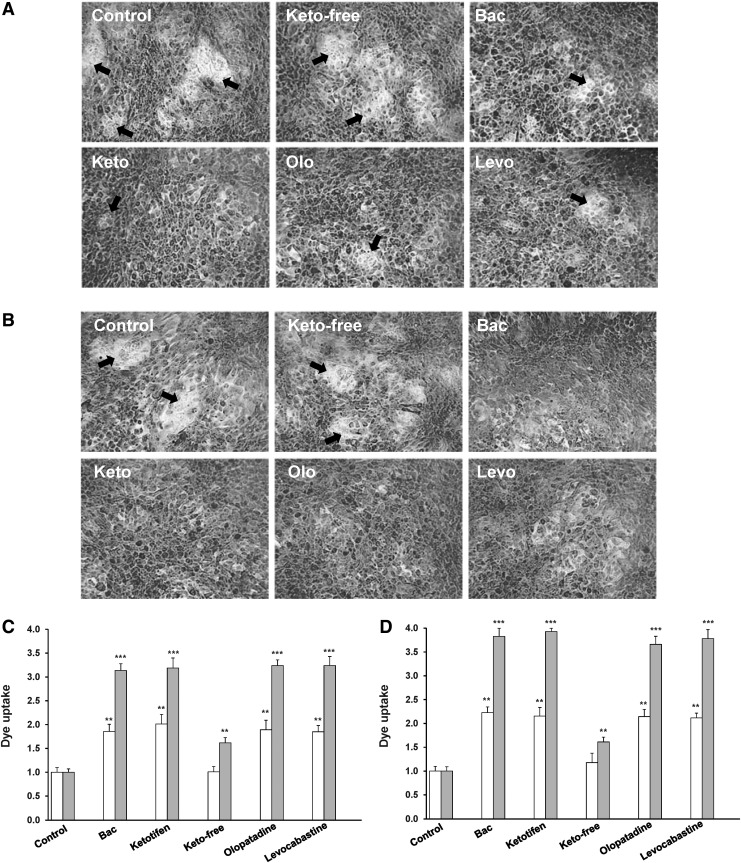
FIG. 4.
Rose bengal penetration in control stratified human corneal epithelial cells and cells treated with the anti-allergic formulations. HCLE cells were exposed to anti-allergic solutions and rose bengal penetration was examined by confocal microscopy. Images were obtained using a 10×objective lens and processed for rose bengal penetration quantification using the ImageJ software. Representative images for 10% anti-allergic drugs are shown in the upper panel: (A) after 1 h of exposure and (B) at 3 h of exposure. Arrows indicate cell regions that exclude rose bengal. Bars represent rose bengal uptake (integrated density of stained areas normalized to control conditions) at 1 h (white bars) and 3 h (gray bars) when HCLE cells were exposed to solutions diluted 1:10 (10% of anti-allergic formulations) and 0.001% BAC (C) or diluted 1:4 (25% of anti-allergic formulations) and 0.0025% BAC (D). Experiments were performed in triplicate and represent the mean±standard deviation, **P<0.01 versus control, ***P<0.001 versus control.