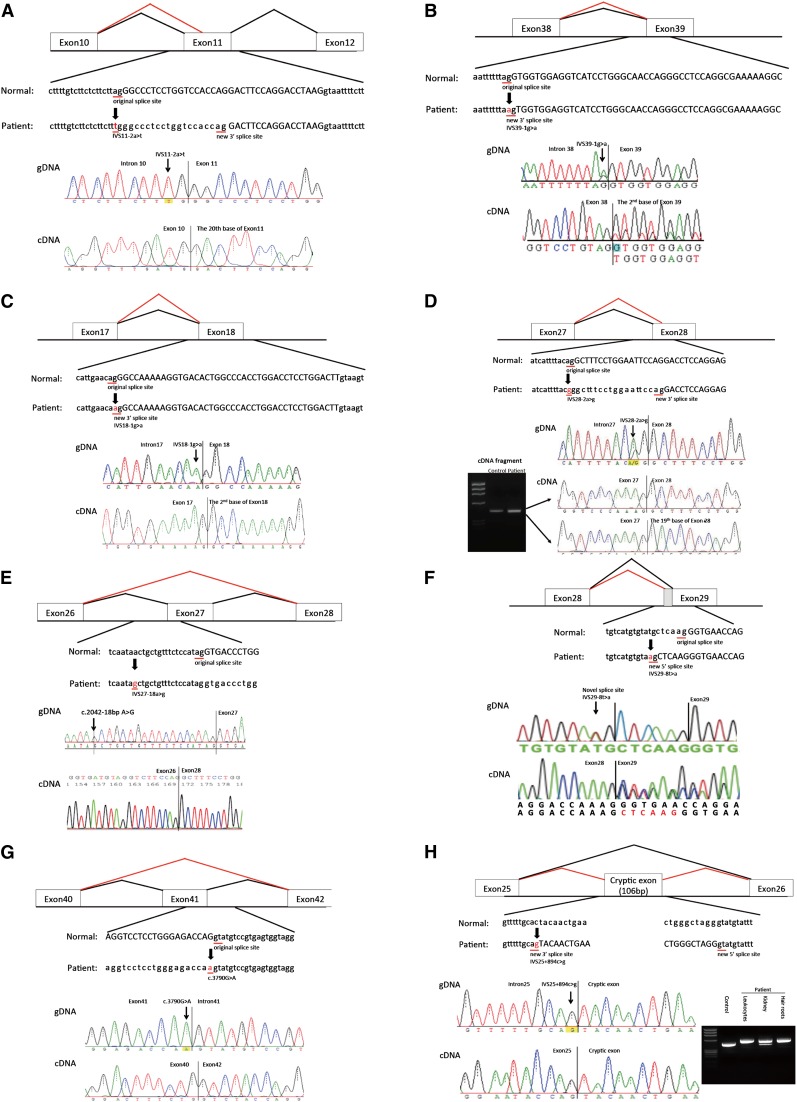
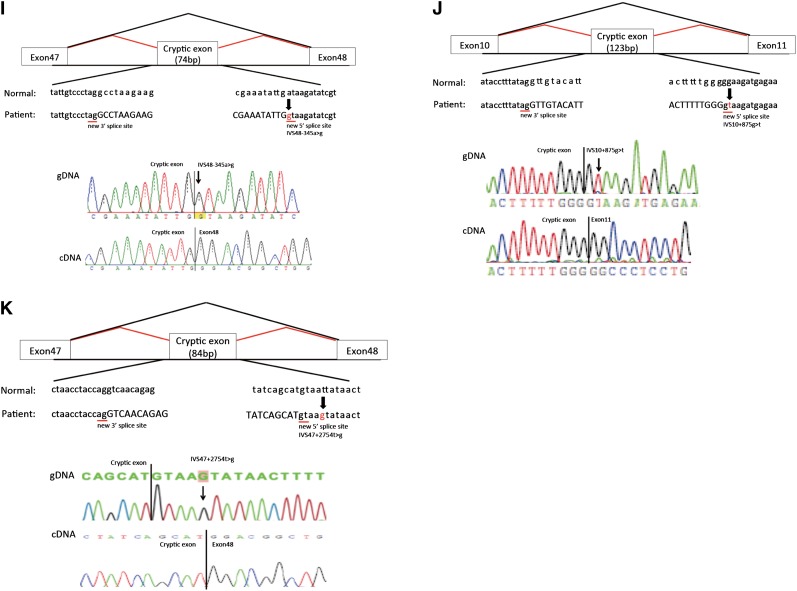
Figure 1.
Mutations and their consequences. Upper panels show schematics of aberrant splicing (red lines). Normal splicing is indicated by black lines. The original and new splice sites and flanking sequences are shown below. A patient’s flanking genomic DNA and cDNA sequences are shown in lower panels. (A) Patient ID 7. IVS11–2A>T eliminated the splice acceptor site of intron 10 to activate a new splice site 19 nucleotides upstream. (B) Patient ID 17. IVS39–1G>A eliminated the splice acceptor site of intron 38, producing a transcript with a 1-bp deletion. (C) Patient ID 27. IVS18–1G>A removed the splice acceptor site of intron 17, generating a transcript with a 1-bp deletion. (D) Patient ID 28. IVS28–2A>G altered the splice acceptor site of intron 27, producing an 18-bp deletion in mature transcripts. (E) Patient ID 128. IVS27–18A>G potentially disrupted the splice acceptor site of intron 26, resulting in exon 27 skipping, which creates a transcript 105-bp deletion. (F) Patient ID 158. IVS29–8T>A changed the splice acceptor site of intron 28 to IVS29–7, which creates a transcript 6-bp insertion. (G) Patient ID 21. The last nucleotide of exon 41 mutation, C3790G>A, disrupted the splice donor site of intron 41, resulting in exon 41 skipping, which creates a transcript with a 186-bp deletion. (H) Patient ID 19. IVS25+894C>G produced a new splice acceptor site, resulting in a cryptic exon activation between exons 25 and 26 and creating a transcript with a 106-bp insertion that contains a stop codon. Lower right panel shows RT-PCR products from leukocytes, kidneys, and hair roots. Only the transcript from the kidney shows a normal-sized band, meaning that the kidney produced both abnormal and normal transcripts without a cryptic exon. (I) Patient ID 48. IVS48–345A>G made a new splice donor site, resulting in the production of a cryptic exon between exons 47 and 48, which creates a transcript with a 74-bp insertion that contains a stop codon. (J) Patient ID 126. IVS10+875G>T made a new splicing donor site, resulting in the production of a cryptic exon between exons 10 and 11 and creating a transcript with a 123-bp insertion that contains a stop codon. (K) Patient ID 217. IVS47+2754T>G made a new splicing donor site, resulting in the production of a cryptic exon between exons 47 and 48, which creates a transcript 84-bp insertion that contains a stop codon. IVS, intervening sequence.