Figure 1.
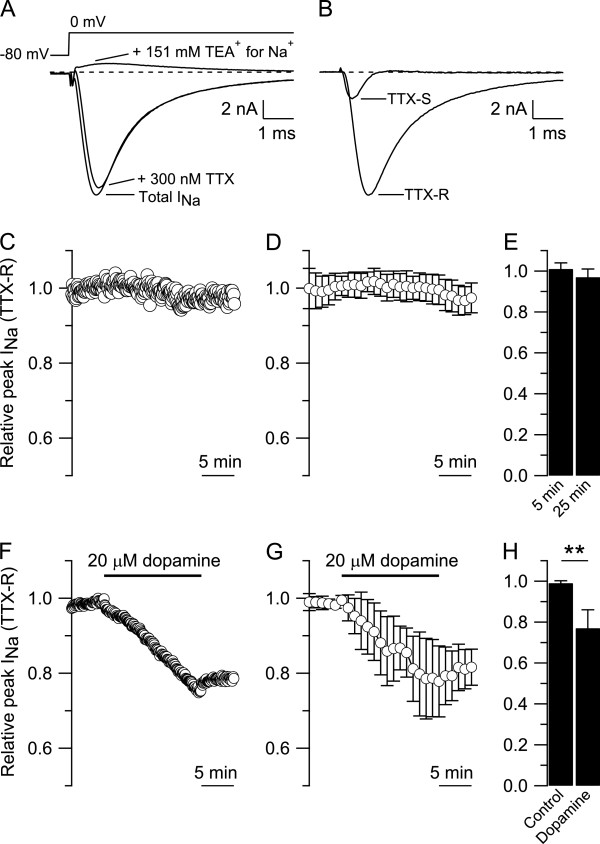
Dopamine effect on TTX-R sodium current. A) Isolation of TTX-R sodium current from a small DRG neuron (diameter ≤ 25 μm). Top: voltage clamp protocol. A single step of voltage from −80 to 0 mV, 30 msec duration, was delivered every 5 sec. Bottom: Total sodium current (Total INa) recorded in Tyrode’s solution supplemented with 30 μM CdCl2 to block calcium current. Subsequent application of 300 nM tetrodotoxin blocked the TTX-S sodium current leaving only the TTX-R sodium current which was completely blocked when 151 mM NaCl was replaced by equimolar concentration of tetraethylammonium-Cl. B) TTX-S and TTX-R sodium currents isolated by subtraction from the cell in A. C) The TTX-R sodium current recorded in a small DRG neuron was normalized to the peak TTX-R sodium current recorded during the first 5 min in whole-cell and monitored for 25 min. D) Collected results showing the relative peak of TTX-R sodium current during 25 min. E) The relative peak of TTX-R sodium current was 1.01 ± 0.03 at 5 min and 0.97 ± 0.04 at 25 min (n = 11, paired t-Test, p = 0.104). F) In a small DRG neuron, 20 μM dopamine reduced the relative peak of TTX-R sodium current from 0.99 (after 5 min in control) to 0.75 (after 15 min in 20 μM dopamine). G) Collected results showing the effect of 20 μM dopamine on the relative peak of TTX-R sodium current. H) The relative peak of TTX-R sodium current was reduced from 0.99 ± 0.01 after 5 min in control to 0.77 ± 0.09 (n = 7, paired t-test, **p < 0.01) after 15 min in 20 μM dopamine.
