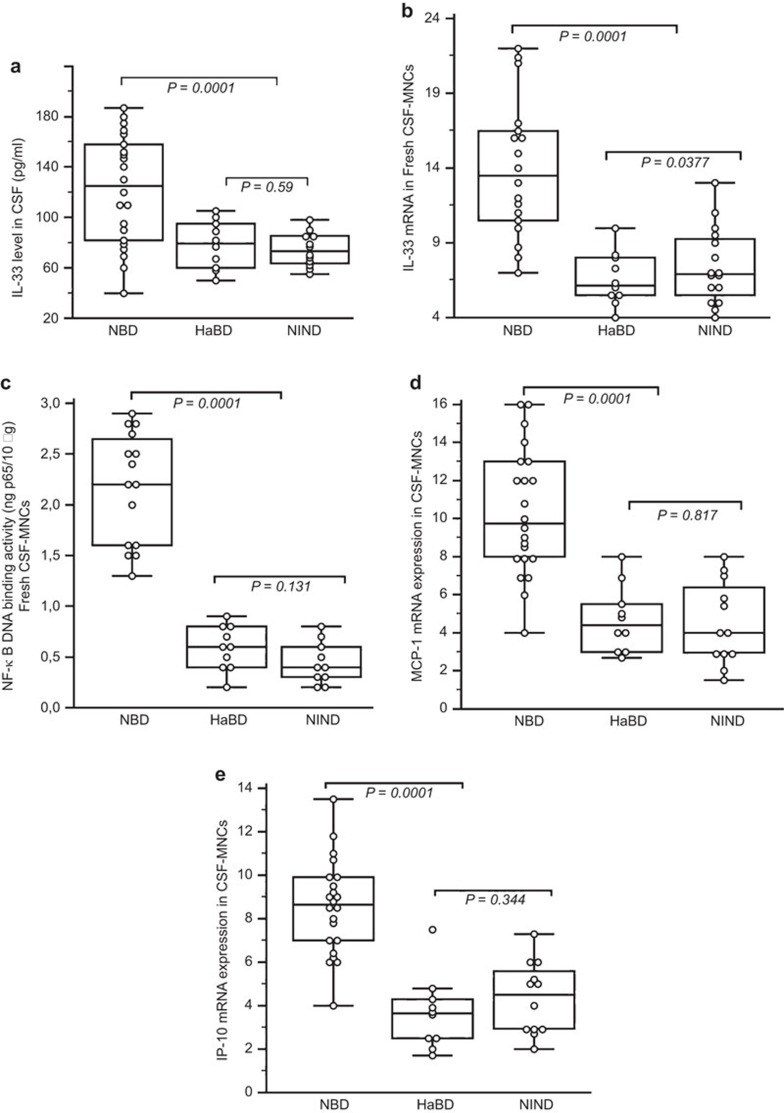
Figure 1.
Expression of IL-33 in cerebrospinal fluid cells from patients with NBD. (a, b) The IL-33 level in CSF and IL-33 mRNA expression in CSF MNCs of NBD patients. The relative mRNA levels of IL-33 are normalized to GAPDH and expressed in AUs. IL-33 in CSF and IL-33 mRNA were highly expressed in NBD patients compared to HaBD and NIND patients. Pearson correlation test showed an association between the CSF IL-33 level and IL-33 mRNA expression (r=0.820; P<0.0001). (c) NF-κB activation in CSF MNCs from NBD patients and control diseases. The NF-κB DNA binding activity is reported as ng of bound p65 protein per 10 µg of total protein in nuclear extracts. NF-κB activation correlated with IL-33 mRNA expression in NBD patients (r=0.739; P=0.00016). (d, e) MCP-1 and IP-10 chemokine mRNA expression in CSF MNCs of NBD patients (15 patients tested). The MCP-1 and IP-10 mRNAs were highly expressed in NBD compared to HaBD (10) and NIND (10) patients. Significant correlations were observed between IL-33 mRNA expression and MCP-1 (r=0.689; P=0.0015) and IL-33 mRNA expression and IP-10 (r=0.753; P=0.0003) in NBD patients. In the figures, the median is indicated by a line inside each box, the 25th and 75th percentiles are indicated by box limits, and the lower and upper error bars represent the 10th and 90th percentiles, respectively. The data in the text are presented as the mean±s.d. Values were compared using Kruskal–Wallis analysis with Dunn's correlation for multiple testing. AU, arbitrary unit; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; HaBD, headache attributed to Behçet's disease; MNC, mononuclear cell; NBD, neuro-Behcet's disease; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NIND, non-inflammatory neurological disease; s.d., standard deviation.