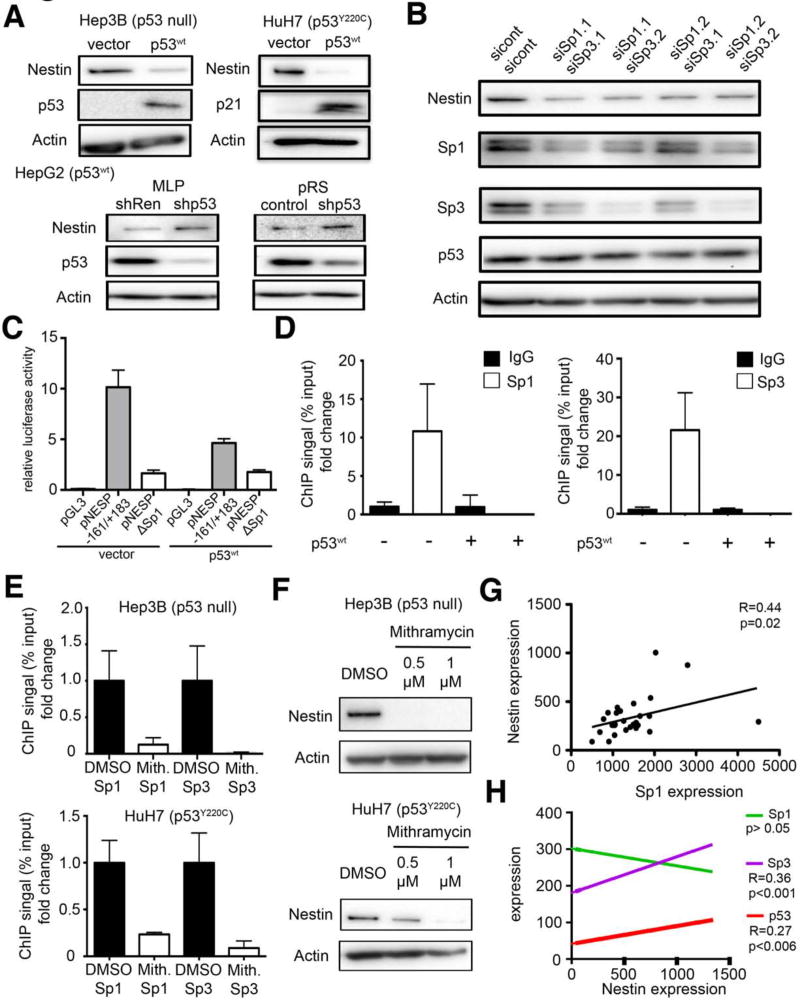
Figure 4. p53 regulates nestin expression in a Sp1/Sp3 dependent manner.
(A) Nestin protein expression in Hep3B and HuH7 cells infected with a vector expressing p53wt or an empty vector (vector) and in HepG2 cells after RNAi mediated p53 knockdown. p53 and p21 expression confirmed functional wildtype p53 expression. (B) Immunoblot for Nestin after siRNA knockdown of Sp1 and Sp3 in HuH7 cells.. (C) Luciferase assay of murine Nestin promoter constructs in the presence or absence of wild-type p53 in NIH3T3 cells (D) ChIP analysis for Sp1 and Sp3 binding to the Nestin promoter in the presence or absence of wild-type p53 in HuH7 cells (E) ChIP analysis for Sp1 and Sp3 binding to the Nestin promoter 18h after treatment with 1 μM Mithramycin or control (DMSO) in Hep3B and HuH7 cells as indicated. (F) Western blot analysis of Nestin expression in Hep3B and HuH7 cells 48h after Mithramycin treatment. (G) Dot plot showing association of Nestin mRNA expression and Sp1 expression in human HCCs, as determined by Spearman correlation. (H) Association of Nestin mRNA expression with Sp1, Sp3, and p53 mRNA expression in cholangiocarcinomas.. Spearman correlation was used to determine statistical significance. See also Figure S3.