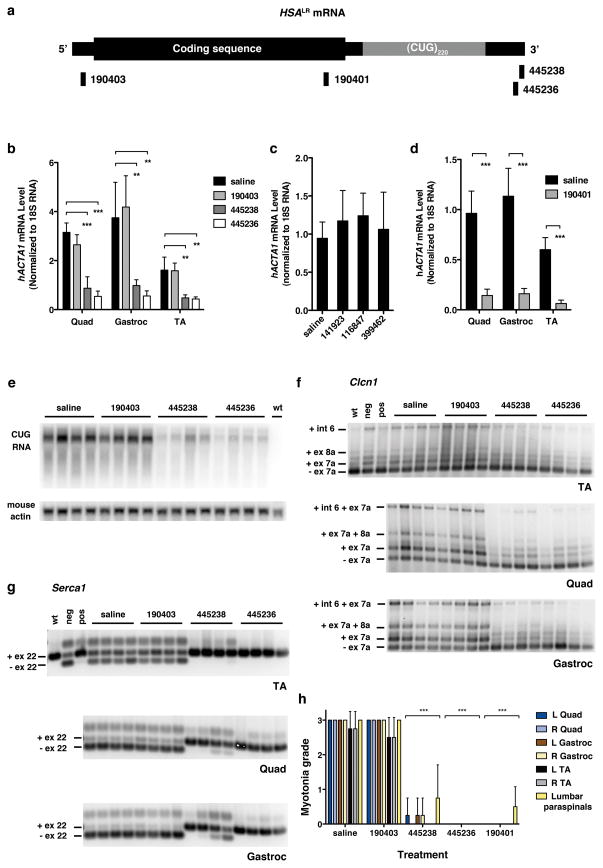
Figure 1. Systemic administration of 2′-O-(2-methoxyethyl) (MOE) ASOs in the HSALR transgenic mouse model of DM1.
a, Location of ASO targeting sequences relative to hACTA1 coding region and expanded CUG repeat in the 3′ UTR. b, Quantitative real-time RT-PCR of hACTA1-CUGexp mRNA in quadriceps, gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior (TA) muscle in HSALR mice treated with the indicated ASOs by subcutaneous injection of 25 mg/kg twice weekly for 4 weeks. Mice were anlayzed 1 week after the final dose (n = 4 per group). Shown are mean levels of transgene mRNA ± SD. ** P < 0.001, *** P < 0.0001 (1-way ANOVA). c, hACTA1-CUGexp transcript levels in quadriceps are not affected by ASOs targeting unrelated transcripts (141923, randomer; 116847, Pten; 399462, Malat-1; n = 4 per group; same dose as b). Error bars ± SD. d, Knockdown of hACTA1-CUGexp mRNA in muscle by ASO 190401 (n = 4 per group; same dose as b). Error bars ± SD. *** P ≤ 0.0005 (t-test). e, Northern analysis of RNA from quadriceps muscle. The level of CUGexp RNA was determined using a (CAG)9 oligonucleotide probe. Mouse actin serves as loading control. f, g, RT-PCR analysis of alternative splicing of Clcn1 (f) and Serca-1 (g) transcripts. For Clcn1, only the −ex7a isoform encodes a functional ion channel. −ex7a, exon 7a skipping; +ex7a, exon 7a inclusion; -ex22, exon 22 skipping; +ex22, exon 22 inclusion; wt, FVB/n wild-type; neg, negative control injected with GAC25 morpholino; pos, positive control injected with CAG25 morpholino. h, Blinded analysis of myotonia by electromyography, 1 week following final dose (n = 4 mice per group). Error bars ± SD. *** P < 0.0001 ASO- vs. saline-treated muscles (2-way ANOVA).