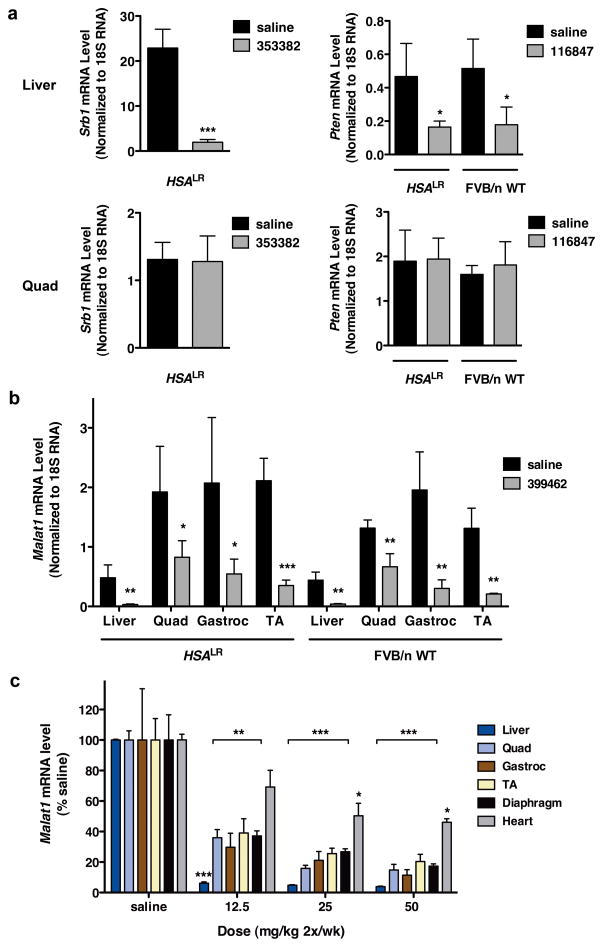
Figure 3. Differential sensitivity of transcripts to ASO knockdown in skeletal muscle.
a, In HSALR or FVB/n wild-type mice, ASOs targeting Srb1 (353382) or Pten (116847) were effective for knockdown in liver but not in quadriceps muscle (qRT-PCR, ± SD; n = 4 per group). * P = 0.02; *** P < 0.0001 (t-test). b, HSALR and FVB/n wild-type mice were treated with ASO 399462 targeting Malat-1, a nuclear-retained lncRNA. Levels of Malat-1 transcript in the indicated tissues were determined by qRT-PCR (± SD). (n = 4 ASO, 3 saline) * P = 0.035; ** P < 0.007; and *** P = 0.001 for ASO vs. saline (t-test). c, Dose response of Malat-1 knockdown in BALB/c wild-type mice. BALB/c wild-type mice were treated with saline or ASO 399462 targeting Malat-1 at 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg twice per week for 3.5 weeks (7 total doses; n = 4 per group). Tissues were collected for RNA isolation two days after the final dose. Malat-1 transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR (± SEM). * P < 0.01; ** P < 0.001; *** P < 0.0001 (2-way ANOVA).