Figure 2.
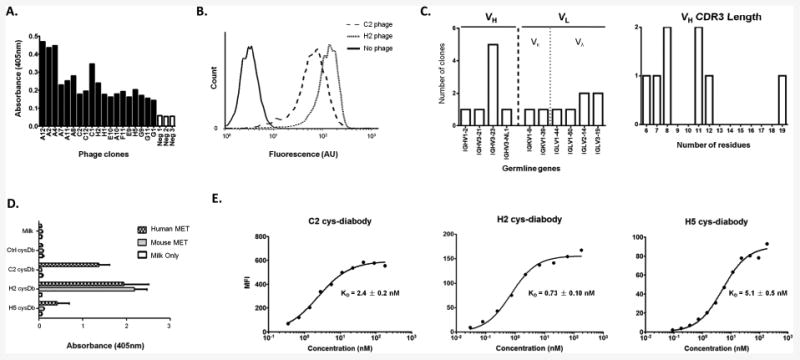
Characterization of anti-MET antibodies. A. Binding of phage clones and controls (helper phage, Neg 1-3) to immobilized antigen (MET) in ELISA. Bound phage were detected with HRP conjugated anti-M13 antibody. B. Binding of two representative phage clones (C2 and H2) to MET-expressing cells by flow cytometry. C. Germline gene usage and the VH CDR3 lengths of the eight clones which bound well to MET positive cells. D. Binding of C2, H2 and H5 cys-diabodies (cysDb) to immobilized human and mouse MET in ELISA. Only the H2 cys-diabody showed cross-reactivity, while C2 and H5 bind to human MET exclusively. Non-specific cysDb (ctrl cysDb) and secondary Ab only were included as controls. E. The affinities of C2, H2 and H5 cys-diabodies were estimated by flow cytometry using MET expressing Hcc827-GR6 cells. The binding curves were fitted in Graphpad Prism to calculate the dissociation constants (KD) using the “one site-specific binding” model.
