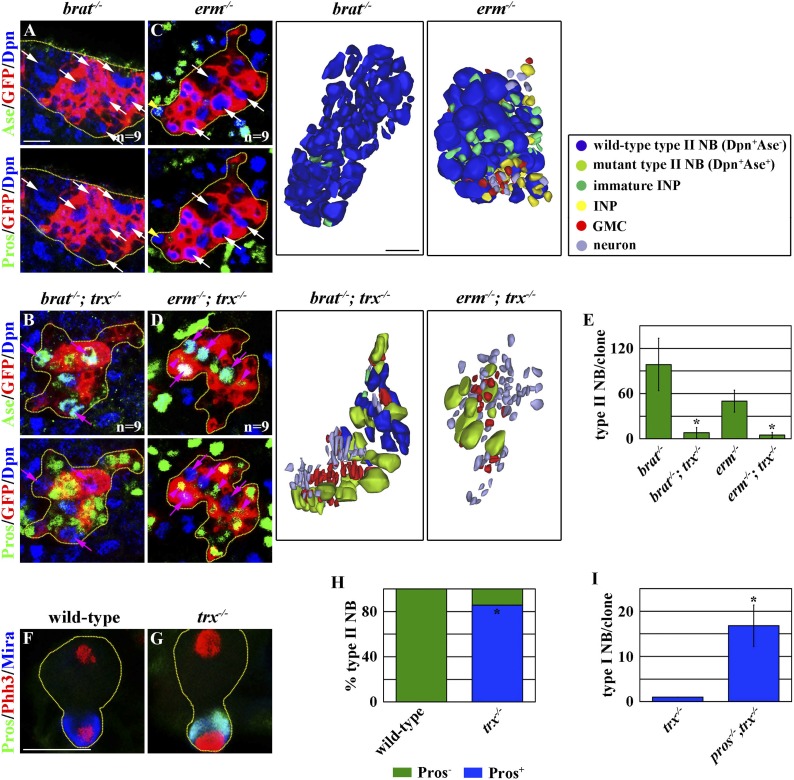
Figure 2. trx mutant type II neuroblast directly generates GMCs.
(A–E) trx is required for the expansion of supernumerary type II neuroblasts in the brat or erm mutant. (A–D) Removing trx function suppresses the expansion of supernumerary type II neuroblasts and restores differentiation in the 96-hr brat or erm mutant type II neuroblast clones. Three-dimensionally reconstructed images of the clones are shown to the right. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) The average number of type II neuroblasts per clone of the indicated genotypes. (F–I) trx mutant type II neuroblasts exclusively distribute Pros to their progenies to specify GMC identity. (F–G) In the 48-hr clones, a wild-type type II neuroblast shows undetectable expression of Pros in telophase, whereas a trx mutant type II neuroblast shows the basal cortical localization of Pros. Scale bar, 10 μm. (H) The frequency of wild-type or trx mutant mitotic type II neuroblasts displaying the basal localization of Pros. (I) The average number of type I neuroblasts per type II neuroblast clone of the indicated genotypes at 72 hr after clone induction.