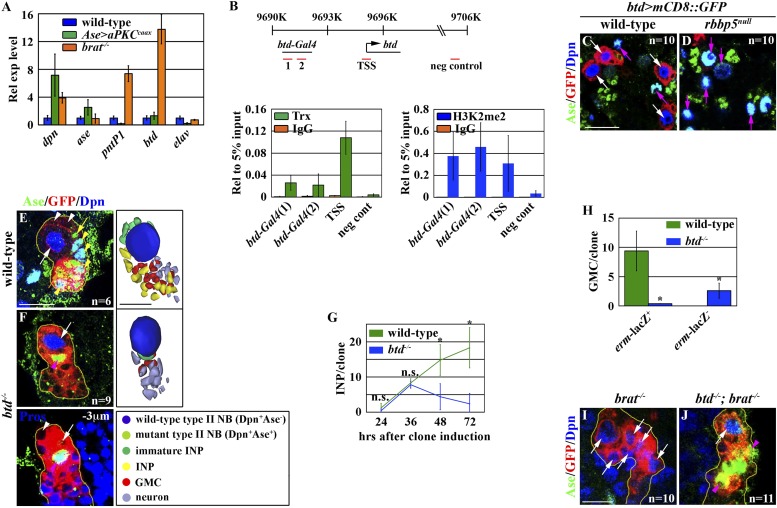
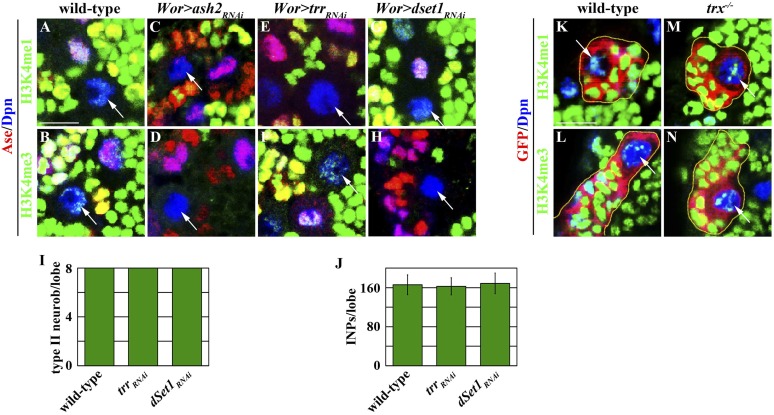
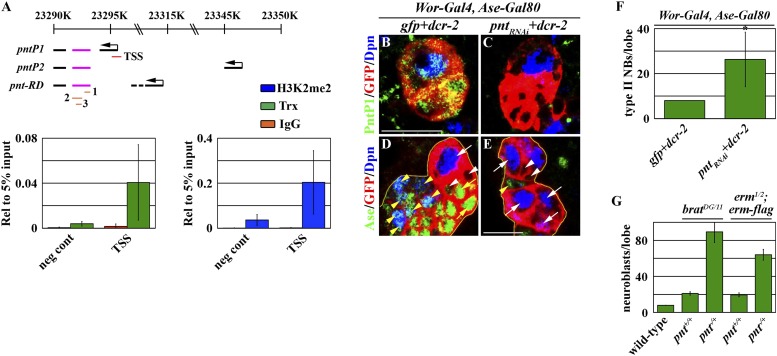
Figure 4. Btd likely acts downstream of Trx to maintain a type II neuroblast functional identity.
(A–D) The btd gene is an excellent candidate target of Trx in the type II neuroblast. (A) The btd mRNA is highly enriched in the lysate extracted from larval brain enriched with type II neuroblasts. The elav transcript is highly enriched in differentiated neurons. The quantification represents the average of three biological replicates. (B) Trx directly binds to the type II neuroblast-specific enhancer element as well as the transcription start site (TSS) of the btd gene. The ChIP experiments were performed using the extract isolated from dissected brat mutant brains that are enriched with type II neuroblasts. Quantification of chromatin immunoprecipitated by the indicated antibodies relative to 5% of input. The quantification represents the average of three biological replicates. (C–D) An enhancer element from the btd gene is sufficient to induce type II neuroblast-specific expression of a UAS-mCD8::gfp reporter transgene in wild-type brain, while the enhancer activity of btd-Gal4 was reduced in rbbp5null brain. Scale bar, 20 μm. (E–H) btd is required for maintaining the functional identity but not the molecular signature of a type II neuroblast. (E–F) In the 72-hr clones, btd mutant type II neuroblasts maintain a type II neuroblast marker expression profile and are surrounded by 1–2 immature INP-like cells. Three-dimensionally reconstructed images of the clones are shown below. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) The average number of INPs per clone of the indicated genotypes. (H) The average number of GMCs with or without erm-lacZ expression per type II neuroblast clones of the indicated genotypes at 72 hr after clone induction. (I–J) The immature INP-like cells generated by btd mutant type II neuroblasts are insensitive to loss of brat function. Removing brat function does not lead to supernumerary neuroblast formation in the 72-hr btd mutant type II neuroblast clones. Scale bar, 10 μm.