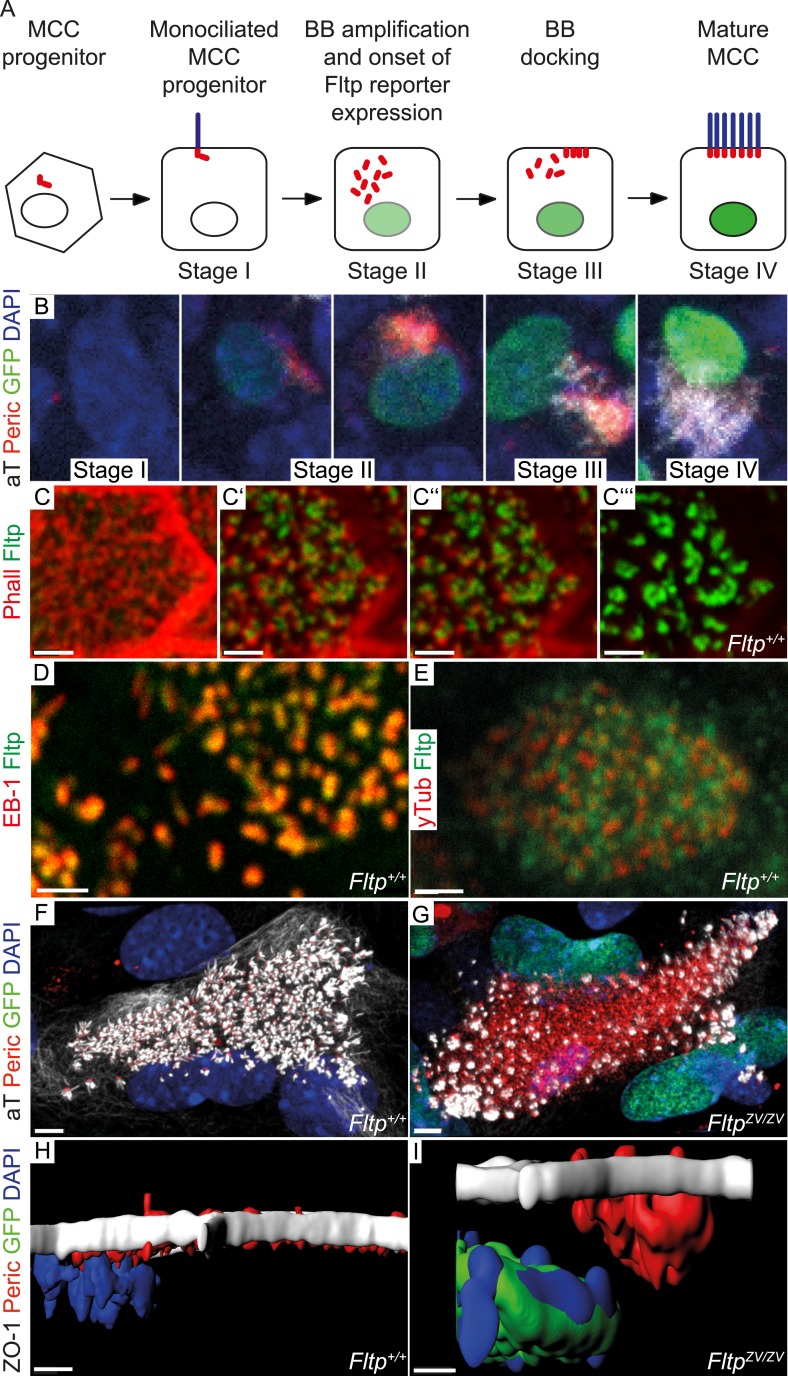
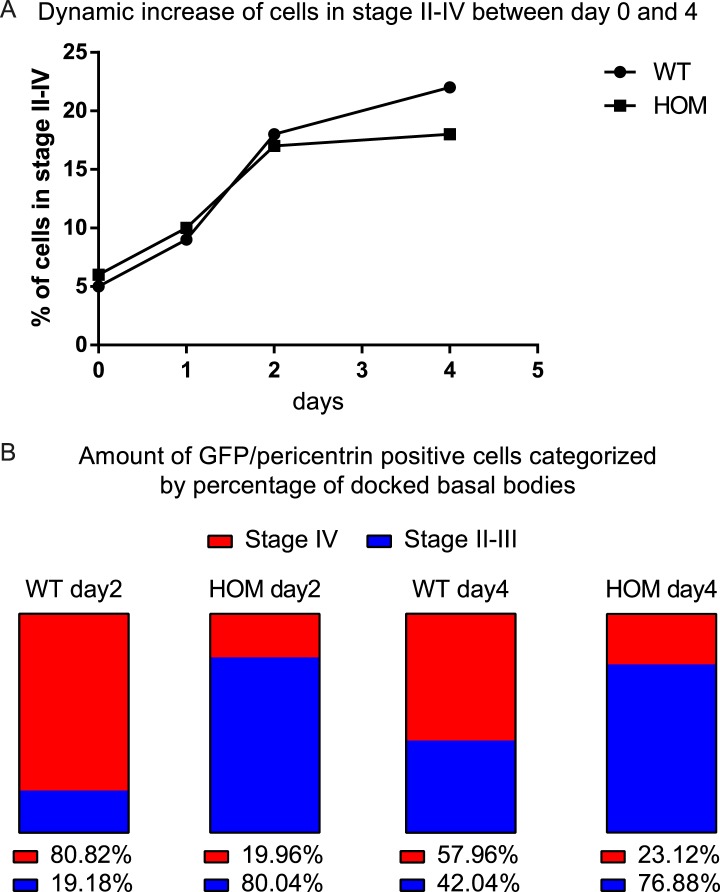
Figure 4. Fltp is expressed and necessary during BB docking.
(A) Scheme of multiciliated cell (MCC) maturation. A MCC progenitor projects a primary cilium at the apical surface (stage I). Centrosome amplification is the first sign of differentiation (stage II) followed by apical transport and docking of BBs (stage III). Fully differentiated cells project multiple motile cilia at the apical surface (stage IV). Staging according to Vladar and Stearns (2007). The green nucleus indicates Fltp reporter gene expression. (B–G) LSM of ALI culture of FltpZV and WT mTECs. (B) Onset and level of Fltp reporter expression correlate with the onset of BB amplification and ciliogenesis (stage II–IV) in cultured ALI mTECs as shown in the scheme in (A). (C–C′′′) Confocal sections of a single cell from the sub-apical actin level (C) over the apical actin level (C′ and C″) to the cilia level (C′′′) (ALI day 4). Fltp co-localizes with the MT-plus end binding protein EB-1 (D) (ALI day 4) next to the pericentriolar matrix (E) (ALI day 4) and to cilia in multiciliated Fltp+/+ cells (C′′′). (F) Fltp+/+ cell showing all BBs (red dots) projecting cilia (white stripes) at the apical surface (ALI day 4). (G) In many FltpZV/ZV cells the majority of BBs are not docked at the level of tight junctions marked by ZO-1 and do not project cilia (ALI day 4). (H and I) Side view IMARIS surface rendering shows that all BBs are docked at the apical surface in Fltp+/+ (H) (ALI day 4) in contrast to FltpZV/ZV cells where most BBs stay in the cytoplasm (I) (ALI day 4). BBs are marked by γ-Tubulin (γTub) and pericentrin (Peric), cilia and the tubulin network by tyrosinated-Tubulin (Tyr Tub) and acetylated-Tubulin (aT), the actin network by Phalloidin (Phall), MT plus ends by EB-1, Fltp protein by Fltp116-1, nuclei by DAPI, and nuclei of Fltp reporter expressing cells by GFP. Scale bars; 2 µm (C–C′′′, D, E), 5 µm (F and G).