Fig. 4.
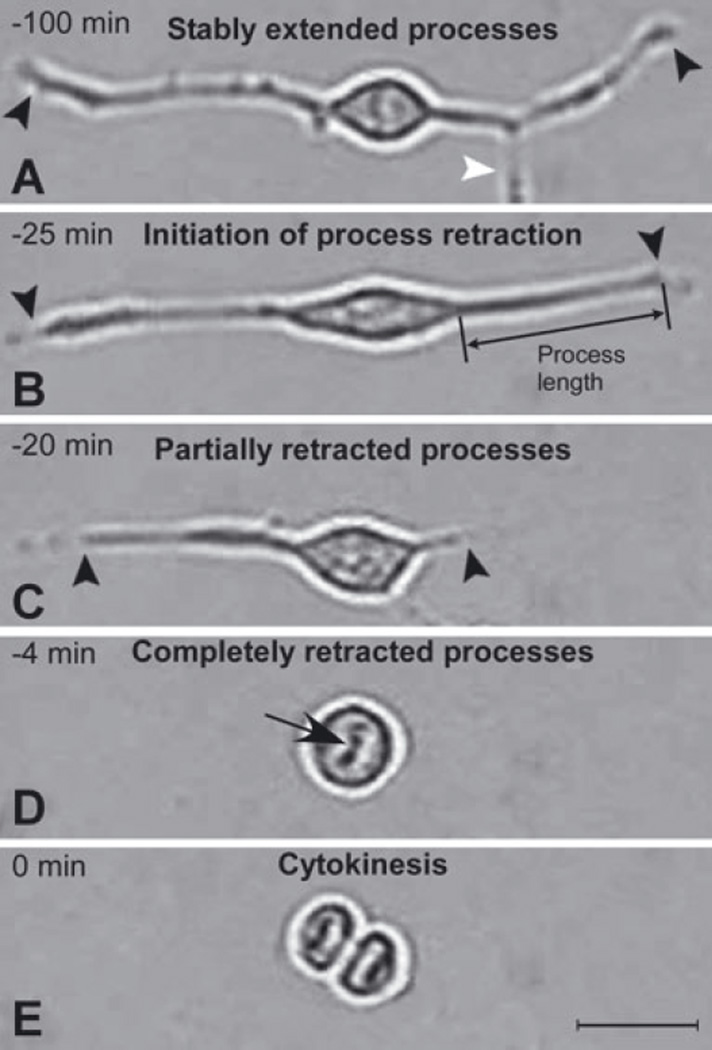
Stages of process retraction and cell cycle progression. Images of a typical dividing SVZa progenitor cell are shown in A–E to illustrate the operational definitions used to determine the progression of process retraction relative to cytokinesis. Black arrowheads in A–C indicate the ends of the cell’s processes and the white arrowhead in A marks a process of another cell, the soma of which is outside the field. The images shown are of a cell in a 5 DIV culture but are representative of cells at earlier and later times in culture. The original videomicroscopic data from which these static images are taken are presented in supplementary Videos S1 and S2 (Cell A). (A) Stably extended processes. For at least 75 min prior to cytokinesis, the length of the processes was relatively stable (< 11% variation in length; compare A with B). (B) Initiation of process retraction. Processes were measured along a straight line from the base of the growth cone to the junction of the process with the soma. At 25 min prior to cytokinesis the processes began to rapidly withdraw, a distinct change in behavior that is defined as ‘initiation of process retraction’. (C) Partially retracted processes. By 20 min prior to cytokinesis the processes are considerably shortened. (D) Completely retracted processes. The time of ‘complete retraction’ is defined as the first time at which an uninterrupted phase-bright ‘halo’ surrounds the cell soma. In contrast, in cells with processes extended there is a break in the halo at the base of processes (e.g. see B and C). Withdrawal of processes continued until they had completely retracted, in this example by 4 min prior to cytokinesis. Note also the chromosomes lined up at the metaphase plate (black arrow; see also supplementary Videos S1 and S2). (E) Cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is defined as the first time at which there is a distinct phase-bright partition separating the two daughter cells. The condensed, aligned chromosomes in the daughter cells can be seen in this image (see also Fig. 2I). Scale bar, 20 µm in E (applies to all panels).