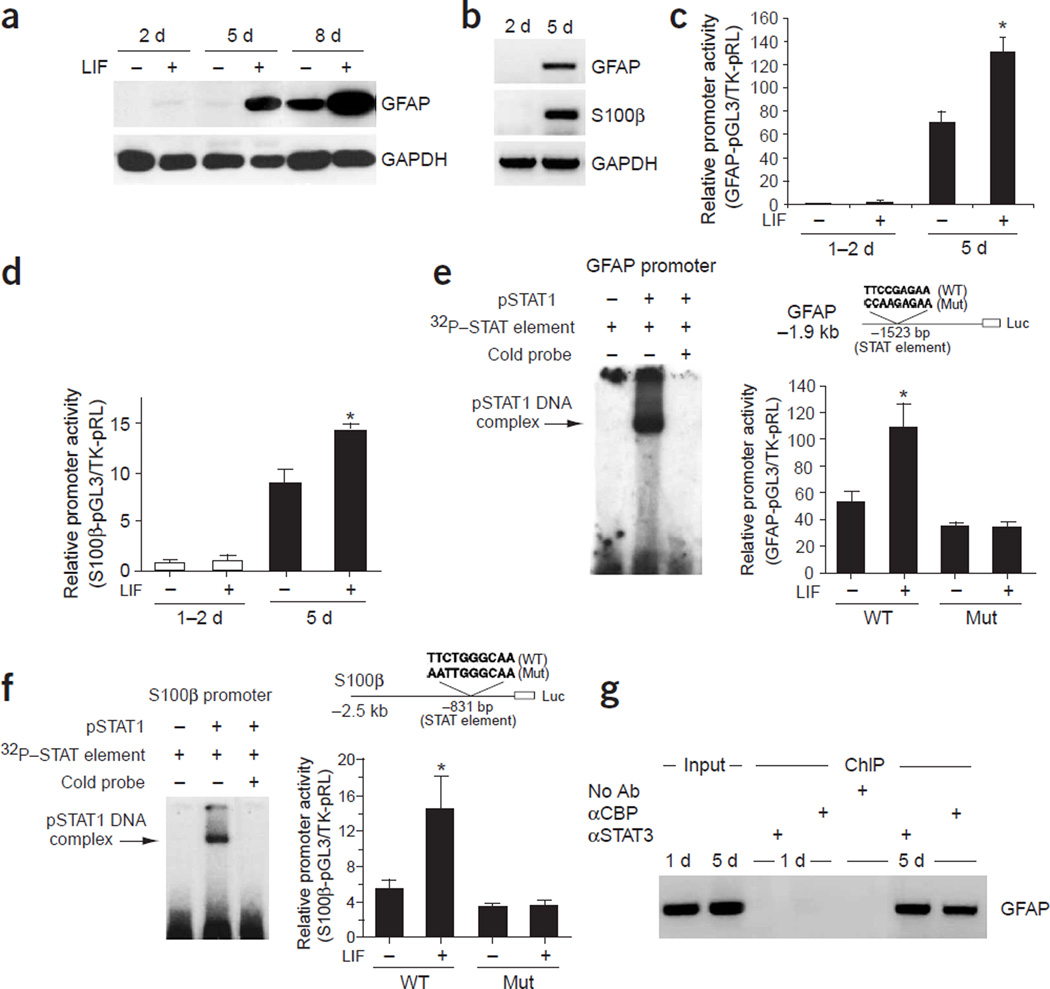
Figure 1.
The late onset of astrocyte differentiation in vitro. (a) Western blot analysis of primary mouse E11 cortical cells cultured for 2, 5, or 8 DIV with or without LIF (100 ng ml−1) continuous treatment. GAPDH signals were used as loading controls. (b) RT-PCR analysis of the expression of astrocytic markers GFAP and S100β, in 2-DIV or 5-DIV cultured E11 cortical cells. GAPDH RT-PCR signals were used as controls. (c,d) 1.9-kb GFAP and 2-kb S100β promoter luciferase reporter constructs were introduced into E11 cortical cells, either untreated or treated with LIF (100 ng ml−1) for 1 d. Luciferase assays were performed between 1 to 2 DIV or at 5 DIV (with transfection and LIF treatment starting 1 d before harvesting) (*, P < 0.05 as compared to the non-LIF treated group, n ≥ 6). (e,f) Bacterially expressed phosphorylated STAT1 (pSTAT1) binds to the STAT binding site (DNA cis-element) within the GFAP and S100β promoters as determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA). Mutation studies of the STAT binding site indicated that STAT cis-elements are required for the activation of glial specific genes by LIF (*, P < 0.05 compared with non-LIF treated group, n ≥ 6). (g) ChIP assay showing that the association of the STAT3/CBP complex with the GFAP promoter is dynamically regulated, which correlates with the gliogenic potential of the cells. The STAT3/CBP complex associates with the GFAP promoter in 5-DIV, but not in 1-DIV cultured E11 cortical cells with 1 d of LIF treatment before cell harvesting. Ab, antibody. α, antibody against (in all figures).