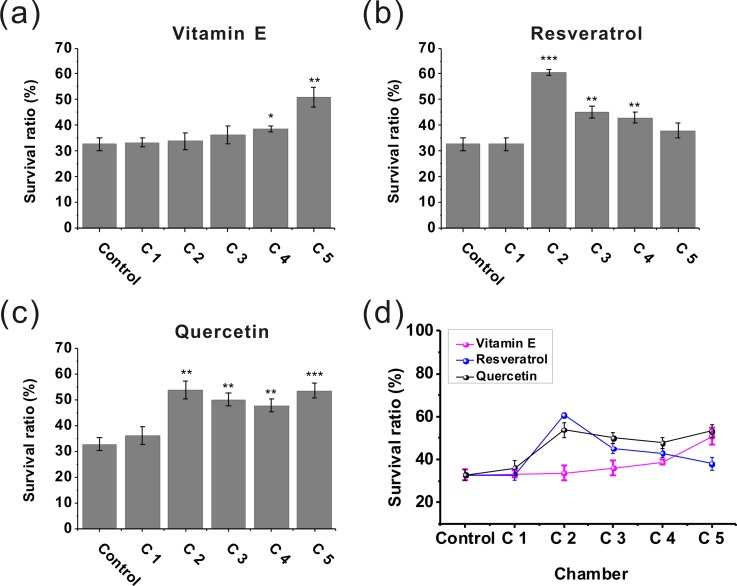
FIG. 9.
The performances of the microfluidic device for estimating the effects of natural antioxidants to protect manganese-induced toxicity. First, the worms were exposed to MnCl2 (100 mM) for 10 h. The survival rates of the exposed worms after treatment with different natural antioxidants of different concentrations in chamber 1–5 were investigated. (a) Vitamin E, (b) Resveratrol, and (c) Quercetin. The asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference from the control group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001). (d) Comparison of the treatment effects of vitamin E, resveratrol, and quercetin. The treatment effect of resveratrol did not rise with the increasing of drug concentration, and we speculated that was because resveratrol of high concentration has certain toxicity for treating Mn-induced neurotoxicity. 20–24 worms used in each assay, 7 days of treatment time, and 3 independent assays under each condition. Error bars denote the SD.