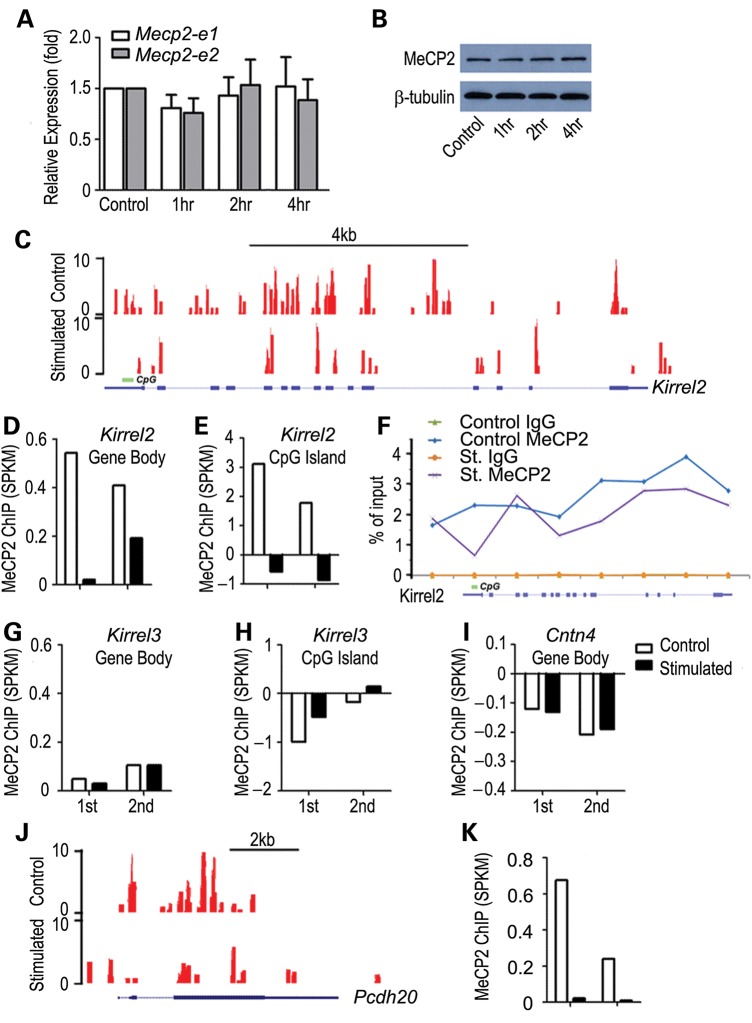
Figure 3.
Odor stimulation results in decreased MeCP2 binding within Kirrel2 and Pcdh20 loci. (A) Mecp2 transcript levels for both Mecp2_e1 and Mecp2_e2 isoforms showed no significant change in either transcript between filtered air control and odor stimulation after 4 h. t-test P > 0.1 (A). Western blotting analysis showed no change in MeCP2 protein in the MOE after acute odor stimulation (B). ChIP-seq analysis of MeCP2 binding in the control filtered air exposed and 4 h complex odor mixture stimulated animals are shown. Example UCSC genome browser tracks of MeCP2 binding to Kirrel2 locus show a widespread binding pattern throughout the gene body (C). Duplicate sets of ChIP-seq reads (1st and 2nd) are mapped and normalized against input. While control mouse datasets show significant MeCP2 binding, odor stimulation results in dramatically reduced MeCP2 binding to the Kirrel2 locus (D). MeCP2 binding to the promoter CpG island of Kirrel2 also shows a sharp drop (E). Eight regions along Kirrel2 locus, including 5′ upstream, promoter CpG, exon and intronic regions, were chosen for quantitative ChIP-PCR analysis. MeCP2 binding to six out of the eight regions decreases consistent with the ChIP-seq analysis (F). No binding was observed with IgG control (green and brown lines in F). No detectable change in MeCP2 binding to the Kirrel3 locus, both throughout the entire locus (G) and at the CpG island (H) is observed. No significant MeCP2 binding to the Cntn4 locus is detected (I). Odorant stimulation does not alter MeCP2 binding within these two gene loci (G and I). MeCP2 binding to the Pcdh20 locus under control condition is also distributed along the entire locus (J). A significant decrease in MeCP2 binding to the Pcdh20 locus was observed under odorant stimulation (J and K). Read counts are shown on the Y-axis in (C) and (J).