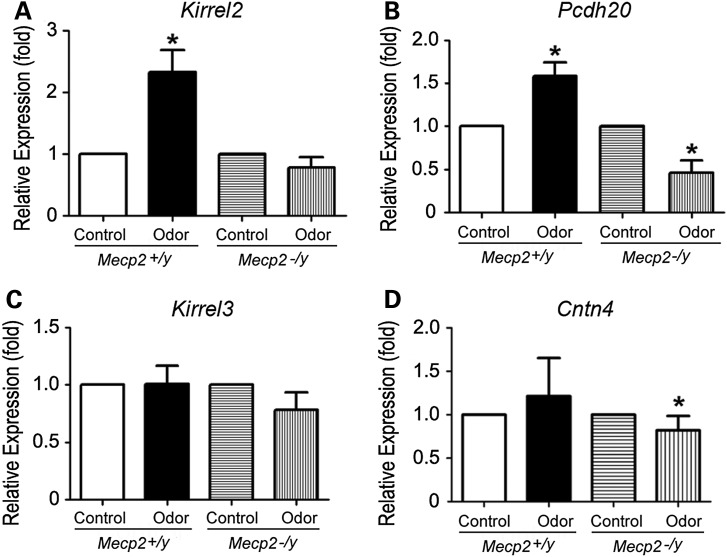
Figure 4.
Mecp2 is the key regulator for odor-evoked Kirrel2 and Pcdh20 expression. Quantitative RT-PCRs for MOE tissues from mice under control filtered air exposure or after 4 h of odor mixture stimulation are performed to compare relative levels of gene expression after normalization against β-III tubulin. In wild-type OE, with control defined as 1, Kirrel2 expression increases significantly after 4 h of odor stimulation (*P < 0.02) compared with the control filtered air exposure. (A) This change in Kirrel2 expression is absent in Mecp2−/y MOE after odor stimulation (P > 0.1, in A). Pcdh20 expression levels decreased (*P < 0.02) after odor stimulation in Mecp2−/y when compared with the control OE, suggesting that the increases in Pcdh20 expression triggered by odor stimulation are regulated by MeCP2 (B). No significant change in Kirrel3 transcript expression is observed after odor stimulation in wild type (P > 0.1) and in Mecp2−/y (C). Though Cntn4 transcript level does not change after odor stimulation in wild type (P > 0.1), there is a decrease after odor stimulation compared with control in Mecp2−/y (*P < 0.02 Student's t-test).