Figure 1.
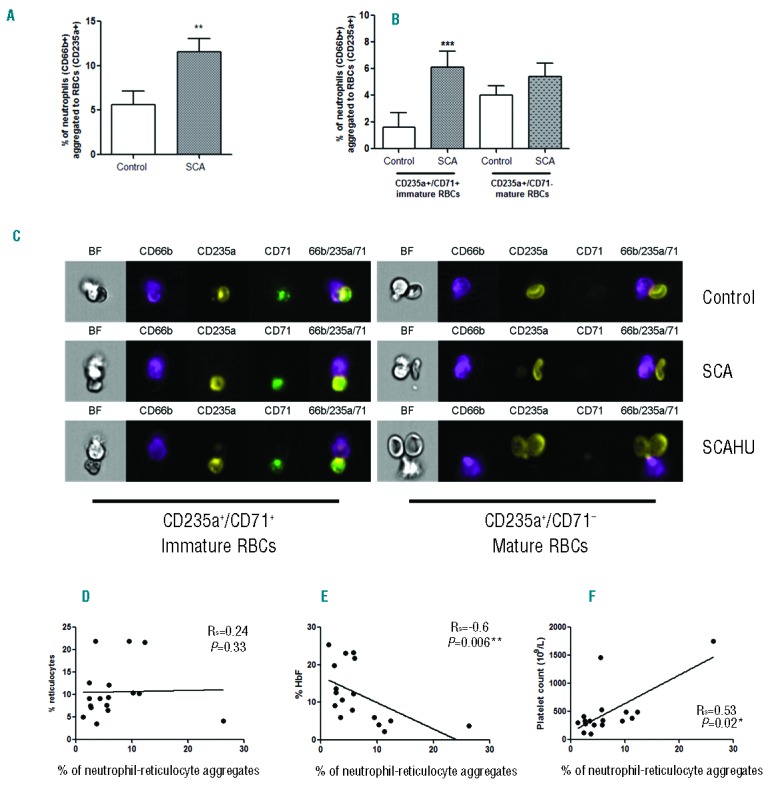
The formation of circulating neutrophil-RBC heterocellular aggregates is augmented in SCA patients. (A) Percentage of neutrophils (CD66b+) aggregated to red blood cells (RBCs) in peripheral blood from healthy individuals (Control, n=11) and SCA patients on/off HU (SCA, n=23), as detected by imaging flow cytometry. **P<0.01, compared to control group (Mann-Whitney test). (B) Percentage of neutrophils (CD66b+) aggregated to immature (CD235a+/CD71+) and mature (CD235a+/CD71−) RBCs in the peripheral blood of healthy individuals (Control, n=11) and SCA patients on/off HU (SCA, n=23), as detected by imaging flow cytometry; ***P<0.001, compared to respective control group (Mann-Whitney test). (C) Representative brightfield (BF) and fluorescent images, acquired by imaging flow cytometry; CD66b+ neutrophils (purple) aggregated to immature RBCs (CD235a+ - yellow; CD71+ - green) or mature RBCs (CD235a+ - yellow; CD71−); Final image: merged CD66b+/CD235a+/CD71+. Cells are from representative samples of peripheral blood from control, SCA and SCAHU patients. (D) Correlation of reticulocyte counts, (E) Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels and (F) platelet counts with percentages of neutrophil-reticulocyte aggregates (CD235a+/CD71+) in SCA (on/off HU) patients (n=17); Spearman’s non-parametric correlation test.
