Abstract
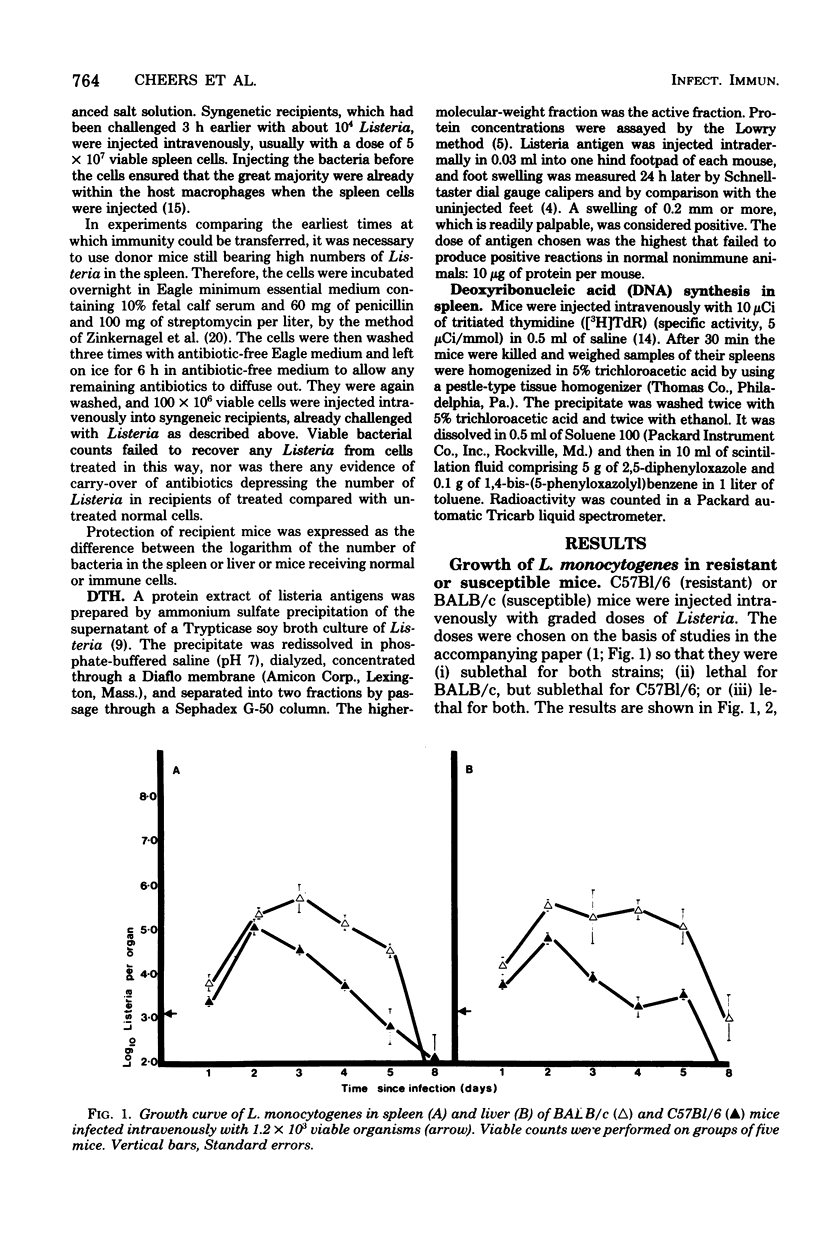
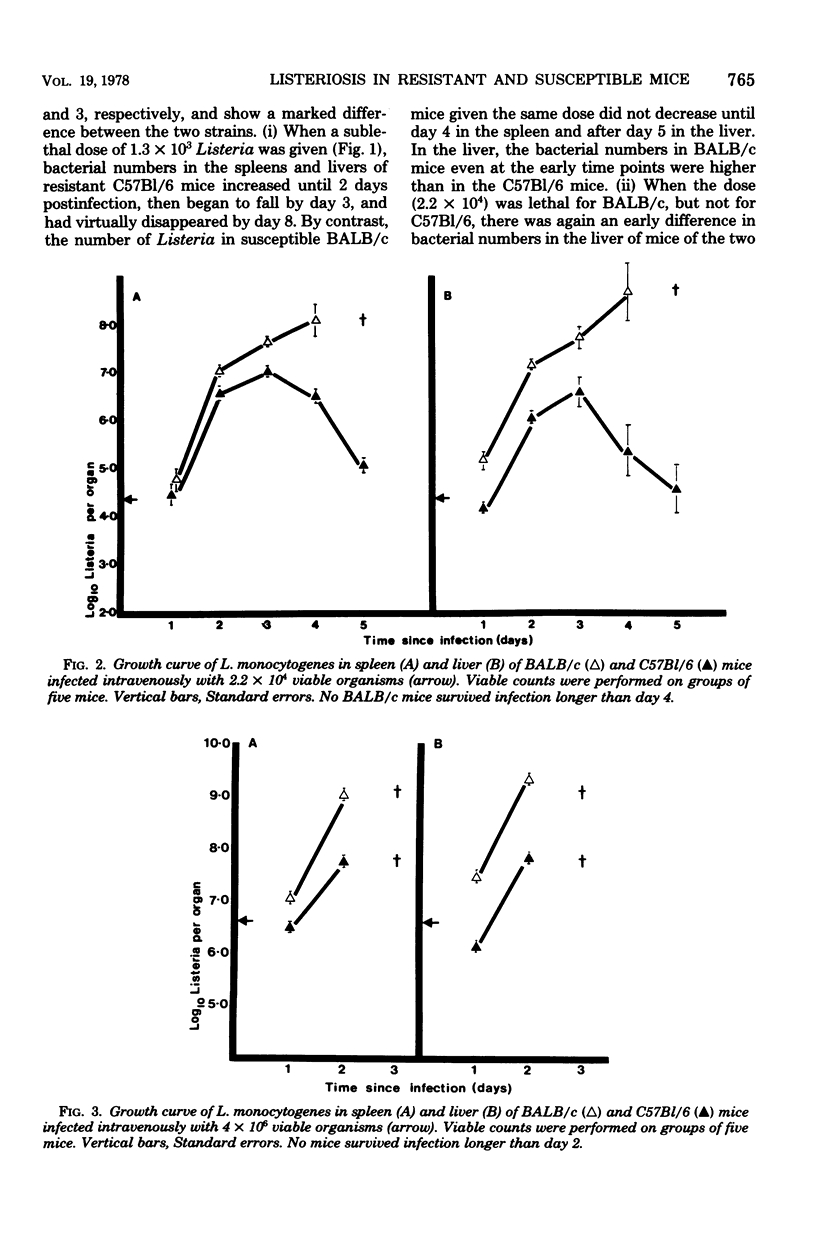
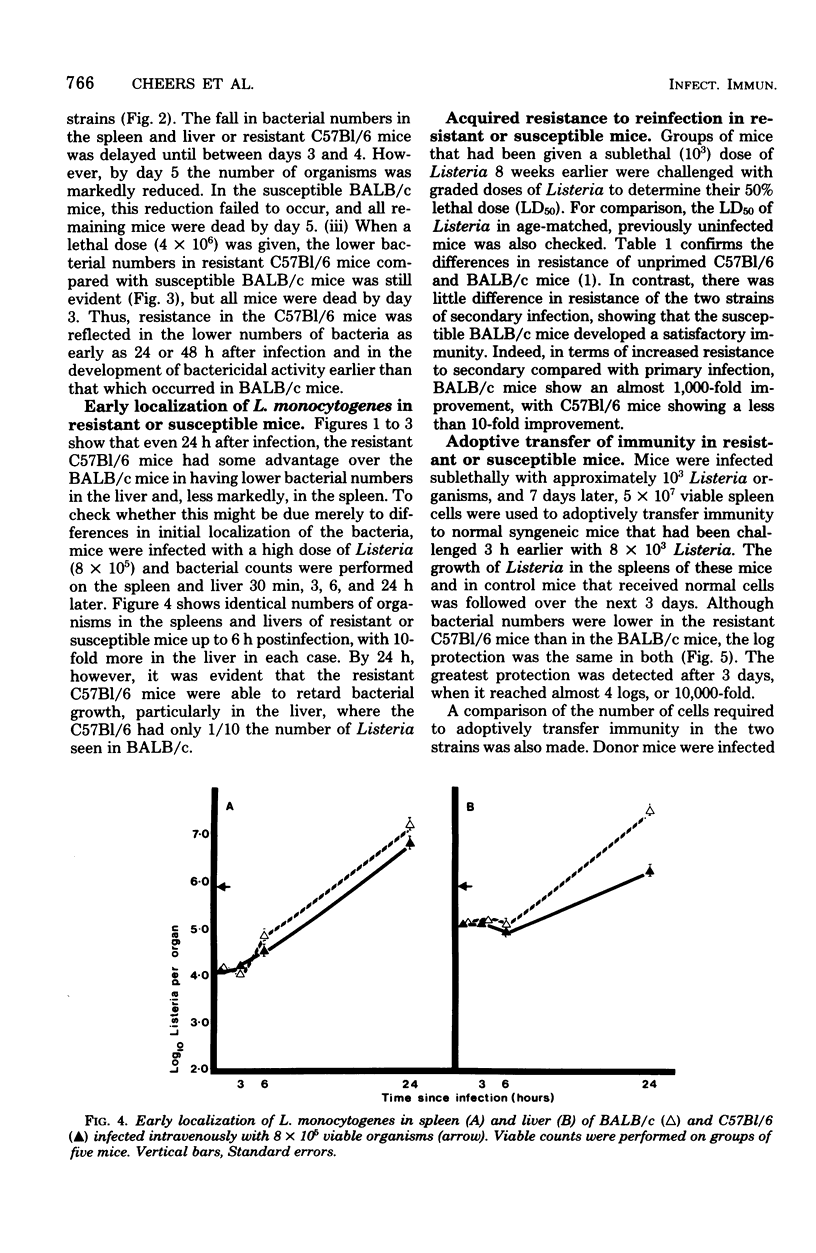
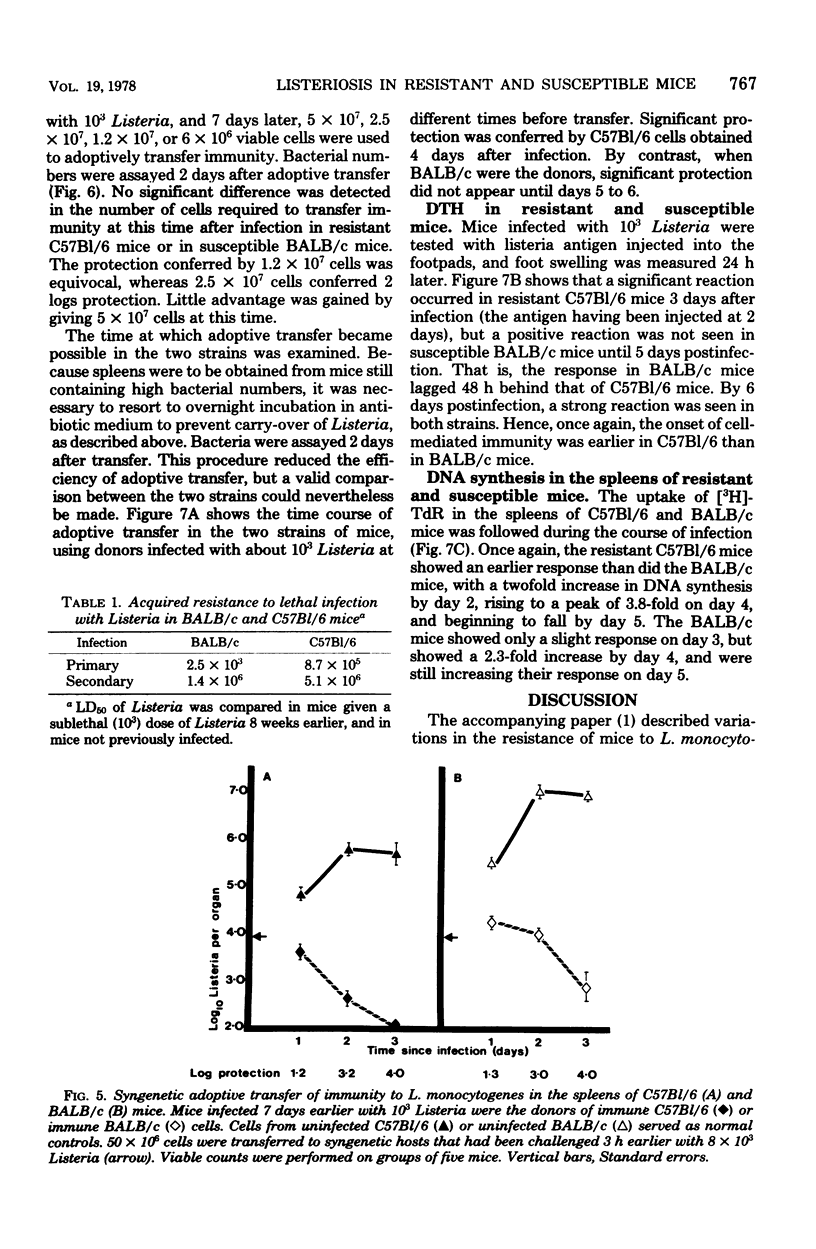
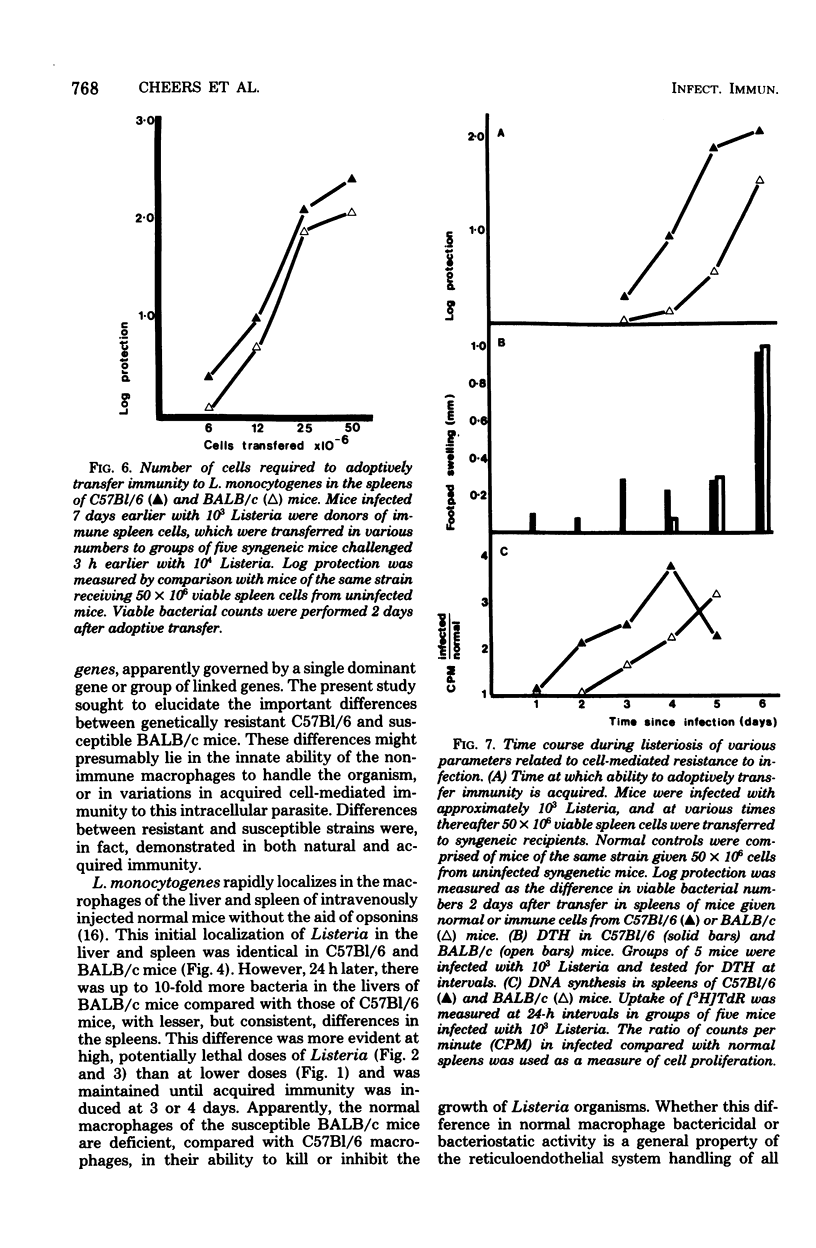
Resistance and susceptibility to Listeria monocytogenes in mice was found to be related to (i) the innate ability of the nonimmune macrophages to kill or inhibit the growth of the organism during the first 24 to 48 h after infection, and (ii) the time of onset of acquired cell-mediated resistance. Resistant C57Bl/6 mice were 10 times more efficient than susceptible BALB/c mice at suppressing the early growth of Listeria in the liver. Furthermore, the onset of acquired immunity occurred 24 to 48 h earlier in C57Bl/6 than in BALB/c mice. Acquired immunity was measured by (i) fall in bacterial numbers in spleen and livers of infected mice (ii) adoptive transfer of immunity to normal mice by using spleen cells from infected mice, (iii) delayed-type hypersensitivity skin testing, and (iv) uptake of tritiated thymidine by lymphocytes in the spleen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. I. Tuberculin sensitivity and resistance to reinfection in BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles R. E., Fajardo I. M., Leibowitch J. L., David J. R. The enhancement of macrophage bacteriostasis by products of activated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):952–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F., JENNINGS P. A. Allergy in experimental mouse tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Aug;72(2):171–195. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKI K., MACKANESS G. B. THE PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:93–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina S., Vas S. I., Robson H. G. Effect of nonspecific stimulation on the defense mechanisms of inbred mice. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1720–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Remold H. G., David J. R. Characterization of a lymphocyte factor which alters macrophage functions. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):275–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Deissler J. F. Nature of "memory" in T-cell mediated antibacterial immunity: cellular parameters that distinguish between the active immune response and a state of "memory". Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):761–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.761-767.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Mackaness G. B., Elliott R. W. The histogenesis of immunologically committed lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Apr;3(4):680–694. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The action of cortisone acetate on cell-mediated immunity to infection. Suppression of host cell proliferation and alteration of cellular composition of infective foci. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1485–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The action of cortisone acetate on cell-mediated immunity to infection: histogenesis of the lymphoid cell response and selective elimination of committed lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Mar;3(3):501–515. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The mitotic potential of fixed phagocytes in the liver as revealed during the development of cellular immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):315–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Blanden R. V., Langman R. E. Early appearance of sensitized lymphocytes in mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


