Figure 2.
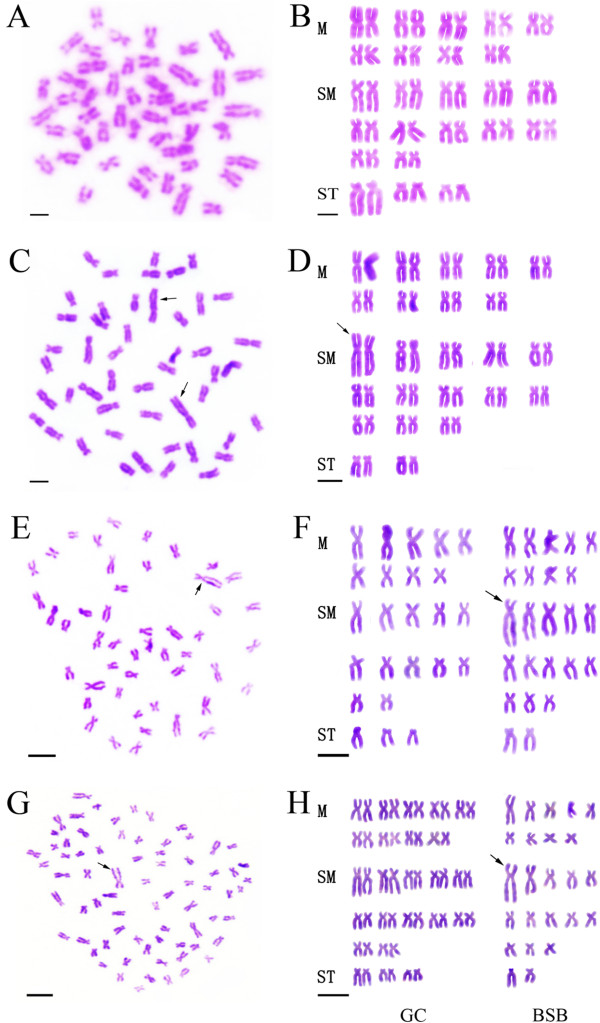
Chromosome spreads at metaphase and corresponding karyotypes of GC, BSB and their hybrid offspring. (A) The 48 chromosomes of GC, with no large submetacentric chromosome. (B) The karyotype of GC, in which no large submetacentric chromosome is detected. (C) The 48 chromosomes of BSB, with a pair of the largest submetacentric chromosomes indicated (solid arrows). (D) The karyotype of BSB, which includes a pair of the largest submetacentric chromosomes (solid arrow). (E) The 48 chromosomes of 2nGB hybrids, with a piece of the largest submetacentric chromosome indicated (solid arrow). (F) The karyotype of 2nGB hybrids, comprising one set of chromosomes from GC and one set from BSB. The solid arrow indicates a piece of the largest submetacentric chromosome, which is similar to that of BSB. (G) The 72 chromosomes of 3nGB hybrids, with a piece of the largest submetacentric chromosome indicated (solid arrow). (H) The karyotype of 3nGB hybrids, consisting of two sets of chromosomes from GC and one set from BSB. The solid arrow indicates a piece of the largest submetacentric chromosome, which is similar to that of BSB. Scale bar in A–H, 3 μm.
