Figure 1.
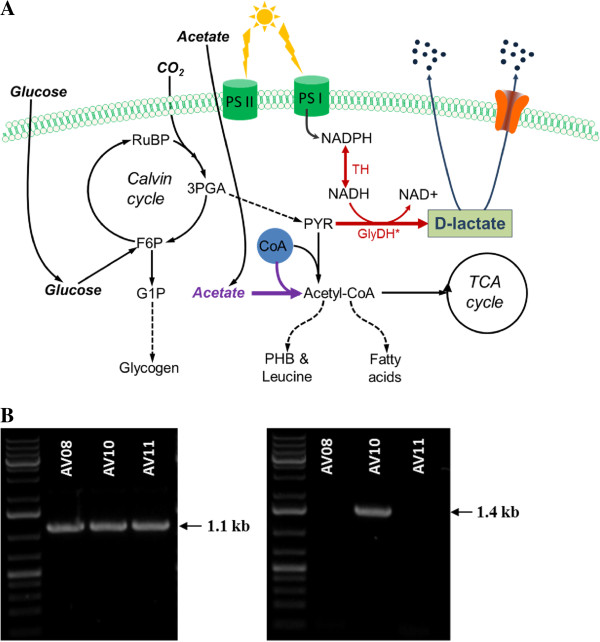
Metabolic engineering of Synechocystis 6803 for the synthesis of D-lactic acid. (A) Metabolic pathway for D-lactate synthesis. Lactate permeation through the cell membrane occurs either via a lactate transporter or by passive diffusion [22,23]. Red arrows indicate the heterologous pathway engineered into Synechocystis 6803. Abbreviations: GlyDH*, mutant glycerol dehydrogenase; TH, Transhydrogenase; 3PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate; CoA, Coenzyme A; G1P, glucose 1-phosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; PHB, poly-β-hydroxybutyrate; RuBP, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. (B) Colony PCR to verify the presence of the heterologous genes of the mutant glycerol dehydrogenase (Left picture) and transhydrogenase (Right picture) in the engineered strains of Synechocystis 6803. gldA101 was amplified with primers gldA-o-F3 and gldA-o-R; gldA101-syn was amplified with primers gldA-o-F and gldA-o-R2; sth was amplified with primers tranNADH-F and tranNADH-R (Table 1).
