FIGURE 2. Activity of the Il7r promoter requires an intact Ets binding site and functional initiator sequences.
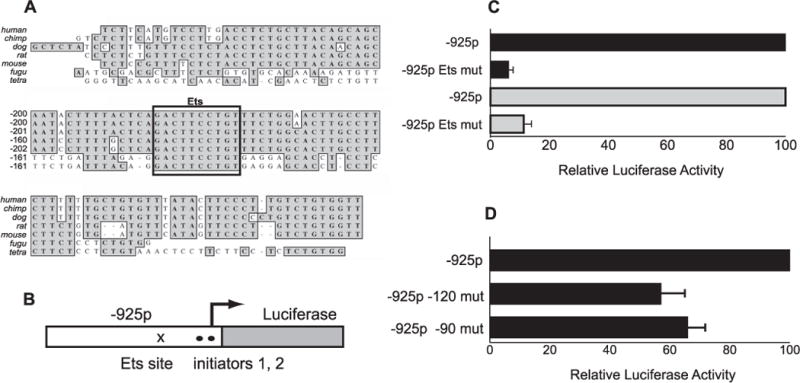
A, the Ets binding site is conserved across multiple species. A ClustalW alignment is shown using Il7r promoter sequences from H. sapiens (human), P. troglodytes (chimp), C. familiaris (dog), R. norvegicus (Rat), M. musculus (mouse), F. rubripes (fugu, i.e. pufferfish), and T. nigroviridis (tetra). The boxed sequence contains the Ets core binding site (TTCC) and conserved flanking sequence. B, overview of luciferase reporter plasmids. The pGL3-IL-7Rα −925 promoter plasmid was modified by site-directed mutagenesis of the Ets binding site (x) or by mutation of putative initiator sequences (●). C, mutation of the Ets site abolishes activity of the Il7r −925 promoter in B and T cells. Plasmids containing a wild type (−925p) or mutant (−925p Ets mut) Il7r −925 promoter were transiently transfected into 38B9 pro-B cells or EL-4 T cells, along with equimolar amounts of a Renilla luciferase plasmid. Results are expressed as % of full activity (normalized firefly luciferase activity of mutant Ets site plasmids/parent plasmids × 100). Error bars represent S.E. ± mean (n = 6). D, effect of initiator mutations on activity of the Il7r promoter. Site-directed mutagenesis of putative initiator sequences was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Plasmids tested contained mutations in putative initiator sequences at positions −120 or −90, and were transiently transfected into 38B9 pro-B cells, along with equimolar amounts of a Renilla luciferase plasmid. Results are expressed as relative luciferase activity (mean normalized firefly luciferase activity of the mutation-containing plasmid divided by the mean normalized firefly luciferase activity of the parent plasmid). Error bars represent S.E. ± mean (n = 6).
