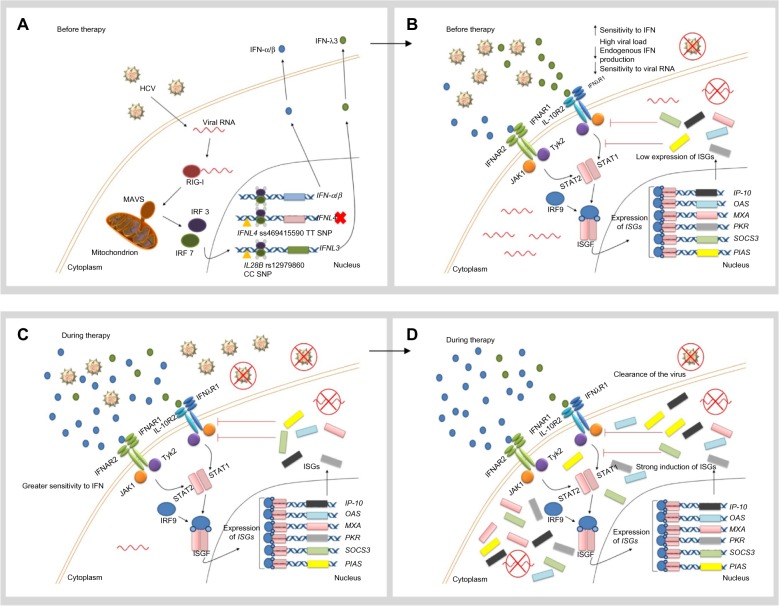
Figure 1.
Hypothetical role of favorable IL28B and IFNL4 genotypes in the response to IFN therapy.
Notes: (A) When the innate immune system, including the RIG-I–IFIH1 pathway, detects the presence of HCV RNA, the adaptor protein MAVS stimulates expression and secretion of IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-λ. In individuals with the favorable IFNL4 genotype, the TT allele creates a frame shift in the gene which inactivates protein expression. In individuals with the favorable IL28B genotype (rs12979860 CC), HCV RNA seems to induce only weak expression of IFN-λ3. (B) IFN-α and IFN-β are recognized by IFNAR, whereas IFN-λ binds to the IL10R-IFNλR receptor complex. Both receptors trigger the JAK-STAT pathway, which induces translocation of an ISGF complex to the nucleus, where it binds to the IFN-stimulated response elements of multiple ISGs. In individuals with the rs12979860 CC genotype, low levels of IFN-λ and therefore weak ISG expression are observed. Despite the fact that this response might be enough to clear the virus at low viral loads, high viral loads can accumulate in the patient. (C) During treatment with IFN-α, the cell is more sensitive to IFN. (D) Therefore, IFN signal transduction is unrestrained and a strong ISG stimulation is detected. Consequently, a more vigorous therapeutic response is developed and the virus can be successfully eliminated. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Hayes CN, Imamura M, Aikata H, Chayama K. Genetics of IL28B and HCV – response to infection and treatment. 2012;9(7):406–417, copyright © 2012.46
Abbreviations: HCV, hepatitis C virus; IFN, interferon; IFIH1, IFN-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1; IFNAR, IFN-α/β receptor 1; IFNL4, interferon lambda 4; L10R, IL-10 receptor; IL28B, interleukin 28B; IFNλR, IFNλ receptor; IP-10, IFN-γ-inducible protein 10; IRF, IFN regulatory factor; ISG, IFN-stimulated gene; ISGF, IFN-stimulated gene factor; JAK, Janus kinase; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MXA, myxovirus resistance protein 1 (also known as MX1); OAS, 2′5′-oligoadenylate synthase; PIAS, protein inhibitor of activated STAT; PKR, protein kinase RNA-activated (also known as EIF2AK2); RIG-I, retinoic-acid inducible protein I; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Tyk2, tyrosine kinase 2.