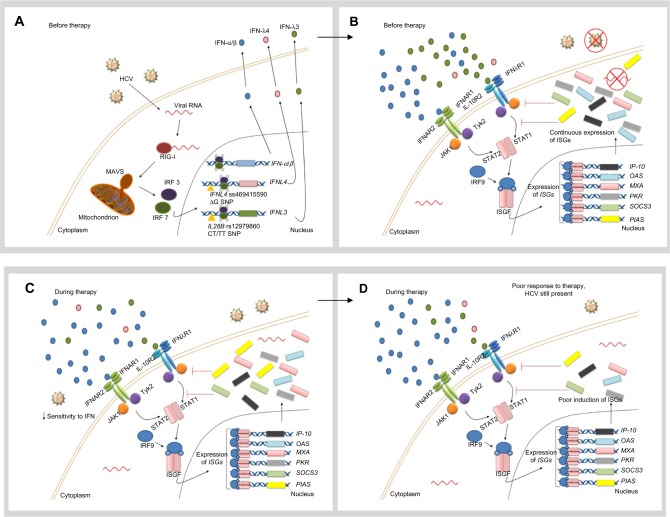
Figure 2.
Hypothetical role of unfavorable IL28B and IFNL4 genotypes in the response to IFN therapy.
Notes: (A) When the innate immune system, including the RIG-I–IFIH1 pathway, detects the presence of HCV RNA, the adaptor protein MAVS stimulates the expression and secretion of IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-λ. In patients with the unfavorable IFNL4 genotype (ΔG allele), the full-length protein is expressed and poorly secreted. On the other hand, constant induction of the IFN signaling pathway in the presence of the virus seems to be a common characteristic in patients with the unfavorable IL28B genotypes (rs12979860 CT/TT). (B) IFN-α and IFN-β are recognized by IFNAR, whereas IFN-λ binds to the IL10R–I IFNλR receptor complex. Both receptors trigger the JAK-STAT pathway, which induces translocation of an ISGF complex to the nucleus, where it binds to the IFN-stimulated response elements of multiple ISGs. The mechanism by which IFN-λ4 impairs HCV clearance remains unclear. In spite of higher baseline ISG expression levels, viral elimination is not possible in patients with the rs12979860 CT/TT genotypes, due to the fact that negative regulation of the JAK-STAT pathway is being activated at the same time through IFN-inhibitory molecules (SOCS3 and PIAS). (C) When IFN-α is administered as part of therapy in patients with unfavorable IL28B genotypes, the cell shows a low sensitivity to IFN. (D) Exogenous IFN-α is not able to stimulate ISG expression strongly enough to clear the virus. Therefore, the patient exhibits a poor therapeutic response. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Hayes CN, Imamura M, Aikata H, Chayama K. Genetics of IL28B and HCV – response to infection and treatment. 2012;9(7):406–417, copyright © 2012.46
Abbreviations: HCV, hepatitis C virus; IFIH1, IFN-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1; IFNAR, IFN-α/β receptor 1; IFNL4, interferon lambda 4; IL10R, IL-10 receptor; IL28B, interleukin 28B; IFNλR, IFNλ receptor; IP-10, IFN-γ-inducible protein 10; IRF, IFN regulatory factor; ISG, IFN-stimulated gene; ISGF, IFN-stimulated gene factor; JAK, Janus kinase; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; MXA, myxovirus resistance protein 1 (also known as MX1); OAS, 2′5′-oligoadenylate synthase; PIAS, protein inhibitor of activated STAT; PKR, protein kinase RNA-activated (also known as EIF2AK2); RIG-I, retinoic-acid inducible protein I; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Tyk2, tyrosine kinase 2.