Figure 4. bIg-mediated binding and phagocytosis of S. epidermidis by IFN-γ-stimulated monocytes and GM-CSF-differentiated moDCs.
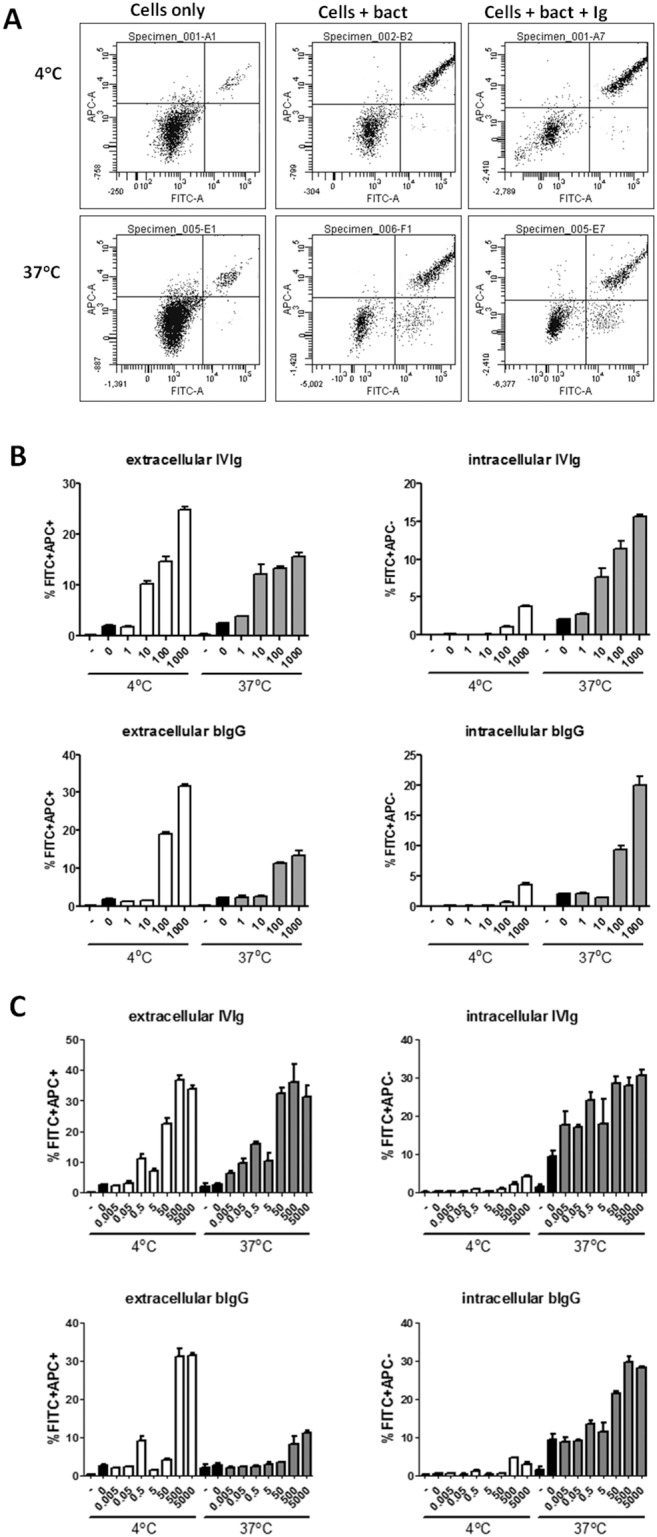
FITC-labelled bacteria were opsonised or not with human (IVIg) or bovine (bIgG) IgG. Subsequently cells were allowed to bind to opsonised bacteria and incubated at 4°C (negative control) or 37°C degrees and stained with APC-conjugated antibodies recognizing FITC. Extracellular bacteria were defined as FITC+APC+ and intracellular bacteria as FITC+APC−. Extracellular bacteria can be observed at both 4°C and 37°C incubated cells, whereas intracellular bacteria are only present in cells incubated at 37°C. A) Example of FACS dot plot and gating strategy. B and C) Percentage of IFN-γ conditioned monocytes (B) and moDCs (C) with extracellular (left) and intracellular (right) bacteria of IVIg (top) and bIgG (bottom) incubated at 4°C or 37°C (indicated at x-axes). Black bars indicate medium (–) or bacteria alone without Ig (0). X-axes show µg/ml Ig used for opsonisation of bacteria. Mean and S.E.M. of triplicate measurements are shown of one out of three donors tested.
